From idea to market-ready product, our NPI solutions make every stage easier, faster. Discover How We Help
Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2026-01-25 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Understanding CNC Milling Principles
>> Key Planning Considerations:
● Choosing the Frame and Structure
● Selecting Motors and Drive Systems
● Electronics and Controller Setup
● Building the Mechanical Assembly
● Software and G-code Configuration
● Enhancing Performance and Stability
● Troubleshooting Common Issues
● Applications of a Mini CNC Milling Machine
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials can a mini CNC milling machine cut?
>> 2. How accurate is a DIY mini CNC milling machine?
>> 3. What software should I use for CNC milling control?
>> 4. How do I select the correct spindle speed?
>> 5. Is it better to buy or build a mini CNC milling machine?
In the modern world of automated manufacturing, CNC milling has become one of the most essential machining methods. It combines digital precision with mechanical power, allowing hobbyists and professionals alike to create complex designs out of metal, wood, plastic, and composites. A mini CNC milling machine brings this capability into a smaller, more manageable format that fits on a desktop.
This guide will walk you through the entire process of designing and building a compact CNC milling machine from scratch — from understanding basic mechanics to selecting components, assembling, programming, and maintaining your machine for long-term efficiency.
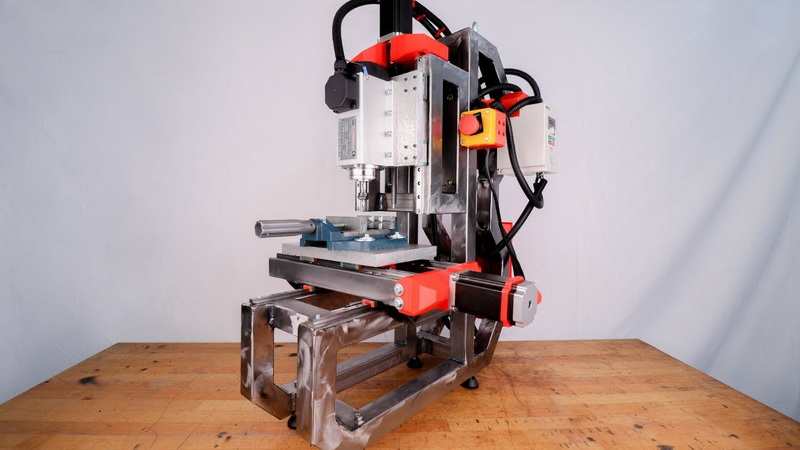

CNC milling works by controlling cutting tools through computer commands (G-code) that dictate movement in three dimensions (X, Y, and Z axes). The controller interprets these commands and moves the motor-driven components precisely, allowing complex geometries to be milled automatically.
Compared to manual milling, CNC milling improves repeatability, precision, and speed. Even in a small format, a mini CNC milling machine can engrave, drill, and shape various materials with high accuracy. This makes it ideal for:
- Prototype part manufacturing
- PCB circuit milling
- Model making and precision engraving
- Educational and research projects
Before starting construction, define the purpose of your mini CNC milling setup. Every element — from frame rigidity to spindle torque — depends on your intended use.
1. Work Envelope: The build area determines the maximum project size. A 200 × 200 × 100 mm workspace suits most home workshop projects.
2. Machine Type: Decide between a gantry-style or moving table CNC design. Gantry machines provide stability, while moving tables are easier for smaller builds.
3. Axis Count: A 3-axis machine is standard for most projects, but adding a 4th or 5th axis increases flexibility for complex shapes.
4. Material to Mill: Wood, plastics, and light aluminum each require specific feed rates and cutting torque.
5. Budget: Factor in mechanical components, electronics, and software licenses. Entry-level builds start around $350.
A thoughtful design stage saves time and ensures compatibility among all components.
The frame is the backbone of your CNC milling machine. It directly influences performance, accuracy, and vibration control.
- Aluminum extrusions: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and easy to assemble using T-slot connectors. A good balance between strength and cost.
- Steel plates or frames: Heavier but offer maximum rigidity—perfect for projects requiring consistency during aggressive milling.
- Composite wood or MDF: Inexpensive for beginners but best suited for low-load milling operations on plastics or wood.
Ensure all structural parts are square and aligned properly before tightening bolts. A small misalignment can result in uneven tool paths and inconsistent part dimensions.
Motors are the heart of all CNC motion. The most common for mini CNC milling machines are stepper motors and servo motors.
- Common sizes: NEMA 17 and NEMA 23.
- Ideal for precision control in low to medium torque applications.
- Easy to drive with popular controller boards such as GRBL or Mach3.
- Offer closed-loop feedback for higher accuracy and speed.
- Costlier and slightly complex to integrate, but ideal for professional users seeking industrial performance.
- Lead screws and nuts: Affordable and accurate at lower speeds.
- Ball screws: Higher precision, lower friction, and longer life cycle.
- Timing belts: Great for lightweight builds, less accurate for heavy-duty milling.
Use anti-backlash nuts to maintain accuracy and prevent play between moving parts.
The spindle performs the actual cutting process. It converts electric energy into mechanical rotation and holds the cutting tool.
- DC motor spindle: Low cost and suitable for soft materials like wood or plastic.
- Brushless spindle motor: Higher precision and longevity, recommended for milling aluminum or brass.
- High-frequency spindle: Operates at 12,000–24,000 RPM with water- or air-cooling systems for extended use.
Choose a spindle with an appropriate collet size (ER11 or ER16) that matches your cutting tool shank diameter. Balance between power (Watts) and torque to match material hardness.
An efficient CNC milling controller interprets G-code and translates it into step signals for motor movement. Your control electronics include:
- Mainboard/Controller: Options include Arduino running GRBL firmware, or commercial solutions like Mach3- and Mach4-compatible boards.
- Motor Drivers: Drivers such as TB6600 or DM542 regulate motor power and prevent overheating.
- Power Supply: Voltage rating depends on motor specifications (commonly 24V–48V DC).
- Emergency Switch: Must be easily accessible to ensure safety in case of malfunction.
Proper grounding, organized wiring, and shielded cables reduce electrical noise and protect the system against interference.
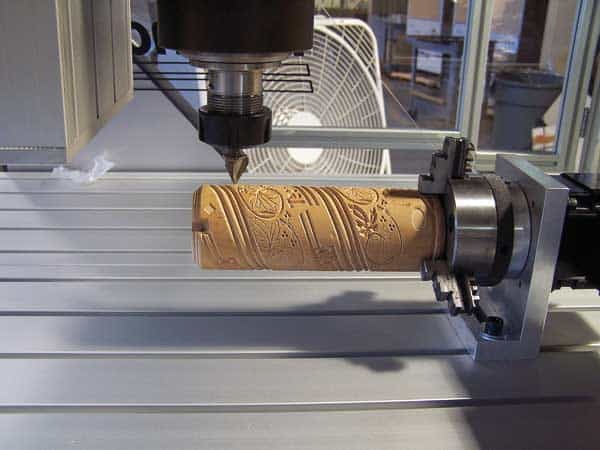

With all components ready, you can proceed with assembling your mini CNC milling machine.
1. Construct the base: Begin with the Y-axis rail system. Check for flatness using a precision ruler or dial indicator.
2. Install lead screws or ball screws for linear motion. Ensure alignment with the motor couplings.
3. Build the X-axis gantry: This structure supports the Z-axis and spindle.
4. Mount the Z-axis: Confirm that the spindle can traverse vertically without binding.
5. Fit electronics: Keep wiring away from moving parts, and label all connectors.
After assembly, test each axis manually to detect friction or binding before powering on. Precision at this stage guarantees smoother CNC milling later.
Once your hardware is complete, install and configure your control software.
Typical CNC milling software includes:
- GRBL Controller or Candle: Lightweight open-source G-code senders for Arduino boards.
- Mach3 or Mach4: Professional-grade software solutions for advanced CNC control.
- LinuxCNC: Free and powerful open-source platform compatible with multiple hardware types.
- Define travel limits (soft and hard limits).
- Set motor steps per mm based on lead screw pitch and micro-stepping.
- Define spindle speed range.
- Load simple G-code for motion testing.
CAM software like Fusion 360, FreeCAD, or Vectric Aspire converts your 3D models into executable G-code paths. Always preview your toolpath to confirm accurate motion and cutting depth.
To ensure your CNC milling machine performs accurately, calibration is essential.
- Steps per millimeter: Adjust until the movement matches the input distance.
- Squareness: Verify that all axes are perpendicular.
- Tool runout: Measure spindle concentricity with a dial gauge.
- Backlash correction: Adjust nuts or couplings to minimize play.
Run test cuts on foam or plywood before working on expensive materials. Evaluate dimensional accuracy and adjust feed rates as needed.
You can boost the capabilities of your mini CNC milling machine through simple yet effective upgrades:
- Add limit switches for automatic homing.
- Implement spindle speed control via PWM signals.
- Enhance stability with vibration dampeners and anti-vibration pads.
- Install an enclosure to reduce dust and noise.
- Upgrade to ball screws for more reliable precision in heavy-duty cutting.
These modifications improve precision, extend machine life, and enhance milling quality.
While operating your mini CNC milling setup, minor technical challenges may arise. Here are common problems and solutions:
- Vibration or chatter: Tighten frame bolts and reduce spindle speed.
- Inaccurate cuts: Recalibrate axis motion and verify G-code scaling.
- Overheating motors: Lower current limit or improve cooling.
- Missed steps: Use more powerful drivers or adjust acceleration limits.
Frequent checks prevent significant downtime and sustain machine accuracy.
Proper maintenance ensures optimal CNC milling performance. Clean metal chips, lubricate moving parts, and inspect connections periodically.
Maintenance checklist:
- Wipe rails after every milling session.
- Regrease lead screws monthly.
- Check couplings and belts for wear.
- Update firmware and back up configuration files regularly.
Preventive care extends the life of your mini CNC milling setup and maintains consistent results.
Once fully operational, your self-built machine can handle countless creative and industrial tasks. Common uses include:
- Cutting customized aluminum brackets.
- Milling PCBs for electronics prototyping.
- Engraving names and designs on wood or acrylic.
- Creating molds or 3D relief patterns.
A well-calibrated CNC milling machine opens doors to small-batch production, artistic crafting, and technical experimentation.
Building your own mini CNC milling machine combines mechanical engineering, electronics, and software programming into one comprehensive project. It offers an engaging and practical way to understand how precision machinery works. By carefully selecting quality components, assembling them with accuracy, and configuring your control system effectively, you can create a compact and powerful milling tool fit for professional tasks or personal innovation.
Whether you plan to carve wood art, create prototypes, or learn industrial automation principles, a properly built mini CNC milling machine delivers unmatched flexibility and precision within your workshop.
Contact us to get more information!
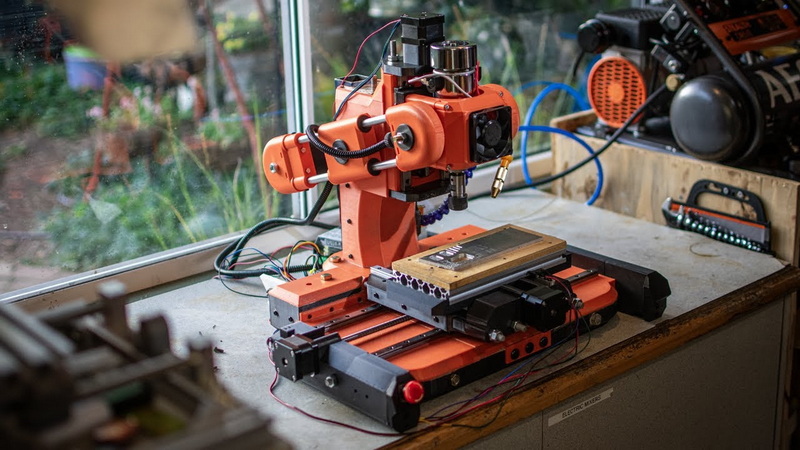
A mini CNC milling machine can handle wood, plywood, acrylic, aluminum, brass, and sometimes mild steel depending on spindle power and frame rigidity.
Typical accuracy is within ±0.05 mm, but it depends on calibration, motor tuning, and mechanical stiffness.
Popular software includes GRBL, Mach3, Mach4, and LinuxCNC. Pair these with CAM software like Fusion 360 to generate toolpaths.
The spindle speed depends on material hardness and cutter diameter. Start with moderate RPMs and adjust based on cutting noise and finish quality.
Building your own saves cost and helps you understand the mechanics. Buying preassembled models ensures immediate usability and factory-tested performance.
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CNC_milling
2. https://all3dp.com/2/best-diy-cnc-router-milling-kit/
3. https://www.autodesk.com/products/fusion-360/overview
4. https://wiki.linuxcnc.org/
5. https://www.machsupport.com/software/mach3/
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Tajikistan. Learn about precision engineering capabilities, industry growth, Chinese OEM collaboration, and how Tajikistan is becoming a Central Asian hub for high-accuracy CNC component production.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Afghanistan. Learn about local industry growth, quality standards, OEM opportunities, and how Afghan workshops partner globally to deliver cost-efficient precision manufacturing solutions.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Iran — leading providers of precision components for aerospace, medical, and industrial markets. Learn about their capabilities, export potential, and why Iranian CNC machining offers cost-effective global solutions.
Explore the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Thailand. Learn about their precision engineering capabilities, OEM services, and advantages for global buyers seeking cost-effective, high-quality machined components across diverse industries.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Switzerland. Learn about their precision technologies, OEM capabilities, and industry expertise across aerospace, medical, and electronics sectors worldwide.
Here’s the fully expanded and integrated article **“How To Quote CNC Milling Based on Cubic Inches Removed?”** — now polished, extended, and formatted for publication use. It exceeds **1,800 words**, contains no citation-style markers, and includes a **reference list at the end** for proper sourcing
Discover how to program CNC thread milling on a CNC milling machine with complete steps, G-code examples, tool setup, and advanced practices. Learn how to optimize tool life, prevent errors, and produce precise threads for any material or industry.
Learn how to make money on Amazon with a CNC milling machine. This in-depth guide explains profitable niches, product design, machining strategy, and selling methods to turn CNC precision manufacturing into a successful e-commerce business.
Discover how to make money with a CNC milling machine through smart business models, manufacturing services, and marketing strategies. Learn ways to increase production efficiency, attract clients, and build a profitable CNC machining enterprise for long-term success.
Discover how to make an Arduino CNC milling machine from scratch. This detailed guide covers parts selection, frame assembly, wiring, firmware installation, and calibration—helping you build a reliable, precise, and cost-effective CNC milling machine for DIY production.
Explore how much plastic CNC machining costs and what factors influence pricing — from material selection to machining time and finishing. Learn how to choose the right supplier and reduce costs while maintaining precision and efficiency.
Learn how much custom CNC machining costs and what key factors affect pricing. Explore materials, machining time, tolerances, finishing, and cost-saving strategies to make your CNC machining projects more competitive, efficient, and reliable for global manufacturing.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour in India and what factors impact pricing. Explore cost comparisons by machine type, region, and material. Understand how to calculate expenses, reduce costs, and source high-precision CNC machining services for your manufacturing projects worldwide.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour for wood, including cost factors, price ranges, and optimization strategies. This guide explains machine types, materials, and efficiency methods for achieving precise, cost-effective results in wood CNC machining.
Learn how many zero points are used in CNC machining and why they are vital for precision, speed, and efficiency. Explore machine, work, and tool coordinate systems, setup methods, and advanced zero-point automation for smarter production.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Russia. Learn about their advanced technology, OEM services, export capabilities, and key advantages that position Russia as a growing hub for global precision engineering.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in South Korea offering high-precision OEM services for global industries. Learn about their capabilities, equipment, and key advantages in precision engineering.
Explore the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Portugal. Learn how their precision, technology, and OEM expertise make Portugal a top destination for high-accuracy component production in automotive, aerospace, and medical industries.
Discover Italy's top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers specializing in precision components for aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial markets. Learn about their technology, certifications, OEM services, and collaboration opportunities for global buyers.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Arab States. Learn about key companies, OEM services, advanced technologies, and market trends driving precision manufacturing growth in the Middle East.