From idea to market-ready product, our NPI solutions make every stage easier, faster. Discover How We Help
Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2026-01-27 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Understanding CNC Machining for Wood
>> Common Wood CNC Machining Applications
● Average Hourly Cost of CNC Machining for Wood
● Cost Factors That Influence CNC Machining Pricing
>> 2. Material Type and Density
>> 4. Programming and Setup Time
>> 5. Tooling Wear and Maintenance
● Comparing CNC Machining with Traditional Woodworking
● Hidden Costs to Consider in Wood CNC Machining
● Cost Optimization Strategies for CNC Machining Wood
● Future Trends in Wood CNC Machining Costs
● Why CNC Machining Is Worth the Cost
● FAQ
>> 1. What type of CNC machine is best for wood?
>> 2. Does CNC machining work well with hardwoods like oak or walnut?
>> 3. What is the average cost difference between outsourcing and in-house CNC machining?
>> 4. Can CNC machining handle both carving and cutting tasks?
>> 5. How can I ensure consistent quality in CNC wood machining?
CNC machining has revolutionized the woodworking industry by combining precision, efficiency, and creative flexibility. Whether making custom furniture, wooden prototypes, architectural elements, or intricate carvings, CNC machining allows woodworkers to produce accurate results with heightened speed and reduced waste.
However, one of the most common questions among woodworking professionals and manufacturing businesses remains: how much does CNC machining cost per hour for wood?
This article provides an in-depth overview of the factors that determine CNC machining costs, explains pricing variations, compares techniques, and offers practical strategies to minimize expenses while maximizing efficiency and quality.
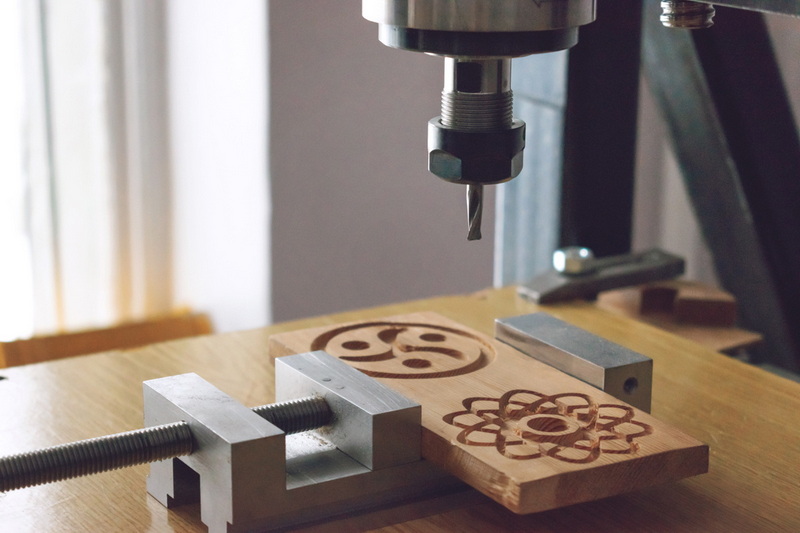

CNC machining (Computer Numerical Control machining) is a subtractive manufacturing process where computer-driven tools shape raw materials into precise forms. In woodworking, CNC machining typically uses routers, mills, or lathes to carve, engrave, drill, or cut wooden materials based on a programmed digital design.
Unlike manual techniques, CNC machining automates much of the labor. The digital commands guide the cutting tools' movement, ensuring consistent results across large production batches. It eliminates human error while providing extraordinary accuracy — often within one-tenth of a millimeter precision.
- Custom furniture production: Cabinets, tables, and chairs with complex joinery and decorative detailing.
- Architectural components: Wall panels, moldings, trims, and decorative facades.
- Musical instruments: CNC machines carve the bodies and necks of guitars or violins with unmatched repeatability.
- Prototyping and signage: Rapid production of 3D wooden models and custom engravings for branding.
In short, CNC machining in woodworking merges craftsmanship and digital innovation, enabling both artistry and industrial precision.
So, how much does CNC machining cost per hour for wood? The answer depends on numerous variables including machine type, labor, design complexity, and shop overhead.
On average, wood CNC machining costs range from $50 to $120 per hour. This broad estimate includes machine usage, operator labor, tooling, and maintenance expenses. Smaller workshops may charge less, while large industrial manufacturers with high-end multi-axis machines often charge more.
| Cost Component | Typical Range (USD/hour) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Machine Operation | $30–$70 | Covers machine wear, electricity, and software depreciation. |
| Skilled Labor | $15–$30 | Operator wages, programming, and supervision. |
| Tooling and Materials | $5–$15 | Includes cutting bits, end mills, and lubricant wear. |
| Overhead | $10–$25 | Facility rent, software licensing, and maintenance. |
When combined, these totals explain the hourly pricing structure of CNC machining. A small woodworking shop may charge $55–$80 per hour, while advanced 5-axis machining centers usually cost upwards of $100–$120 per hour due to higher complexity and setup time.
Understanding the factors behind CNC machining costs helps buyers and producers estimate accurate quotations and identify cost-saving opportunities.
Different machines produce different results — and operate at different costs.
- 3-Axis CNC Routers: The most common for woodworking. Affordable, efficient, and suitable for panels or surface carving.
- 4-Axis Machines: Add rotational capability for cylindrical shaping, used in chair legs or turned parts.
- 5-Axis CNC Machines: Enable cutting at complex angles, ideal for precise 3D contours but come with higher hourly rates and setup complexity.
Generally, as machine capability increases, so does the hourly cost due to greater programming time and tool wear.
Wood density directly impacts machining speed and tool longevity.
- Softwoods (pine, cedar, spruce): Easy to cut, low wear on tools, resulting in lower machining costs.
- Hardwoods (oak, maple, walnut): Dense materials require slower cutting speeds and tougher bits, increasing both time and cost.
- Engineered woods (MDF, plywood): Offer consistent texture but can produce more dust, requiring extra vacuuming or safety precautions.
Simpler geometries cut faster, consume fewer tools, and require minimal setup. Complex or high-tolerance parts demand multiple tool changes, longer roughing passes, or slower feed rates — all of which raise costs.
Adding decorative patterns, 3D reliefs, or tight-fit joints can increase not only design preparation time but also machine runtime per unit.
Before machining begins, the operator must program tool paths, secure the workpiece, and configure cutting parameters. Setup time can take 30 minutes to several hours depending on part complexity.
This setup effort affects small production runs the most, as setup costs are distributed across fewer finished items.
Tools such as end mills, router bits, and drills dull over time. Hardwoods accelerate wear, requiring frequent replacement. Maintaining sharp tools ensures clean cuts and reduces sanding or rework — but each tool replacement adds cost.
Experienced operators charge higher rates, but their precision reduces material waste and downtime. A well-trained CNC machinist maximizes feed speed, minimizes tool breakage, and ensures consistent output, providing long-term savings.
Larger orders reduce average cost per piece. This is because setup and programming expenses are spread across multiple parts. For instance, machining one prototype might cost $100/hour, but an identical run of 500 parts could average only $60/hour.

Traditional woodworking commands artistry, but it cannot match CNC machining's consistency and scalability. Below is a practical comparison:
| Aspect | Traditional Woodworking | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Precision | Dependent on human skill | Highly accurate (±0.1 mm) |
| Speed | Manual and slower | Automated, faster |
| Repeatability | Inconsistent | 100% repeatable results |
| Design Complexity | Limited by hand tools | Handles intricate 3D forms |
| Waste | Higher material loss | Reduced waste via optimized tool paths |
| Initial Investment | Low equipment cost | High upfront CNC acquisition |
For mass production, CNC machining quickly offsets its initial costs through labor efficiency, improved speed, and drastically reduced errors.
Beyond the hourly rate, several hidden charges may influence total cost:
- Material preparation: Cutting blanks or securing fixtures before machining.
- Software licensing: Professional CAD/CAM software like Fusion 360 or SolidWorks adds subscription fees.
- Finishing: Sanding, sealing, or staining after machining may require extra time.
- Scrap loss: Even precise machines occasionally produce unusable pieces during test runs.
- Maintenance downtime: Machine calibration and cleaning reduce available machining hours.
Budgeting for these indirect costs ensures accurate project planning and quote preparation.
Wood manufacturers and machining shops can manage expenses strategically. Implement the following cost-saving methods to improve profitability:
1. Simplify the CAD design. Avoid unnecessary detail levels and small features that prolong machining time.
2. Optimize tool paths. Efficient cutting paths reduce travel distance and cycle time.
3. Use proper bits for each wood type. Selecting correct feed and speed settings reduces breakage and tool wear.
4. Bundle production. Run parts in batches to divide setup time across multiple pieces.
5. Invest in preventive maintenance. A well-calibrated CNC machine minimizes errors and material waste.
6. Outsource wisely. If volume is low, it's cheaper to outsource jobs to specialized CNC machining companies instead of investing in expensive machines.
These tactics maintain high-quality output while keeping operational costs under control.
The global market trend indicates gradual cost stabilization because of technological advancements and wider adoption.
Several developments may influence future pricing:
- Automation & robotics integration: Robots handling material loading/unloading may reduce labor expenses.
- Advanced cutting tools: New coatings and composites extend tool life, lowering replacement costs.
- AI-driven optimization software: Real-time analytics can automatically select ideal feed speeds and depths for minimum cost.
- Eco-friendly manufacturing: CNC machining reduces waste, aligning with sustainable production standards.
As digital manufacturing evolves, CNC machining for wood will likely become even more cost-efficient and accessible to small businesses.
Although CNC machining may appear expensive per hour, the total value it delivers justifies the investment. Its benefits extend far beyond speed — they transform the entire production process:
- Consistency: Every piece is identical, supporting mass production.
- Customization: Quick design changes allow custom or one-off manufacturing without rebuilding jigs.
- Efficiency: Automated processing enables 24/7 operation with minimal oversight.
- Scalability: Businesses can scale production seamlessly without major quality loss.
Instead of measuring price strictly by hourly rates, companies should assess CNC machining as a productivity tool that pays off through longevity, customer satisfaction, and precision.
So, how much does CNC machining cost per hour for wood? On average, woodworking CNC machining runs between $50 and $120 per hour, depending on design complexity, machine equipment, materials, and operator expertise.
While initial costs may appear high compared to manual woodworking, CNC machining ensures guaranteed precision, reduced waste, and scalable productivity. For both small workshops and mass-production facilities, the efficiency and repeatability of CNC machining make it one of the smartest manufacturing investments today.
By simplifying designs, optimizing production batches, and maintaining tools properly, businesses can balance quality and cost effectively — achieving premium results without overspending.
Contact us to get more information!
A 3-axis CNC router is generally the best option for most wood applications. It offers a balance of versatility and cost efficiency, making it ideal for both professional shops and small-scale users.
Yes. CNC machining handles hardwoods accurately, but slower cutting speeds and stronger bits are necessary. This increases machining time slightly, raising the cost per hour compared to softwoods.
Outsourcing small batches may cost slightly more per part but avoids equipment investment and maintenance. Long-term production benefits from owning machines since internal costs per hour drop after depreciation.
Absolutely. CNC machining combines multiple operations — cutting, routing, drilling, and engraving — all under a single program. This eliminates the need for multiple tools or setups.
Use well-maintained machines, apply correct feed speeds and spindle RPMs, and ensure the design file is optimized. Regularly check calibration and use sharp tools for the best finishes.
1. https://www.cnccookbook.com/cnc-router-woodworking-guide/
2. https://makezine.com/projects/what-is-cnc-machining-beginners-guide/
3. https://www.woodworkingnetwork.com
4. https://www.hubs.com/knowledge-base/how-much-does-cnc-machining-cost/
5. https://www.autodesk.com/cnc-machining
Learn how to find workplace coordinates for CNC machining through manual and automated methods. Discover G54–G59 offsets, touch probe usage, and best practices for ensuring precision, accuracy, and repeatability in CNC manufacturing.
Discover how to perform accurate hole-shaft fits in CNC machining. Learn types of fits, tolerance systems, machining steps, precision inspection, and assembly validation to achieve perfect mechanical performance and repeatable dimensional accuracy.
Learn how to determine X Y step in CNC machining with complete calibration methods, formulas, and real examples. This detailed guide explains how to ensure precision motion, improve dimensional accuracy, and maintain long-term machine consistency.
This detailed guide explains how to clean CNC machining tooling marks from plexi edges using sanding, buffing, flame polishing, and vapor polishing techniques. Learn how to prevent edge defects, achieve optical clarity, and maintain pristine CNC-machined acrylic surfaces.
Discover how to automate CNC machining for maximum efficiency, precision, and cost savings. Learn about robotics integration, IoT sensors, AI-driven software, and workflow strategies to transform your manufacturing process into a fully automated, data-powered production system.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Tajikistan. Learn about precision engineering capabilities, industry growth, Chinese OEM collaboration, and how Tajikistan is becoming a Central Asian hub for high-accuracy CNC component production.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Afghanistan. Learn about local industry growth, quality standards, OEM opportunities, and how Afghan workshops partner globally to deliver cost-efficient precision manufacturing solutions.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Iran — leading providers of precision components for aerospace, medical, and industrial markets. Learn about their capabilities, export potential, and why Iranian CNC machining offers cost-effective global solutions.
Explore the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Thailand. Learn about their precision engineering capabilities, OEM services, and advantages for global buyers seeking cost-effective, high-quality machined components across diverse industries.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Switzerland. Learn about their precision technologies, OEM capabilities, and industry expertise across aerospace, medical, and electronics sectors worldwide.
Here’s the fully expanded and integrated article **“How To Quote CNC Milling Based on Cubic Inches Removed?”** — now polished, extended, and formatted for publication use. It exceeds **1,800 words**, contains no citation-style markers, and includes a **reference list at the end** for proper sourcing
Discover how to program CNC thread milling on a CNC milling machine with complete steps, G-code examples, tool setup, and advanced practices. Learn how to optimize tool life, prevent errors, and produce precise threads for any material or industry.
Learn how to make money on Amazon with a CNC milling machine. This in-depth guide explains profitable niches, product design, machining strategy, and selling methods to turn CNC precision manufacturing into a successful e-commerce business.
Discover how to make money with a CNC milling machine through smart business models, manufacturing services, and marketing strategies. Learn ways to increase production efficiency, attract clients, and build a profitable CNC machining enterprise for long-term success.
Discover how to make an Arduino CNC milling machine from scratch. This detailed guide covers parts selection, frame assembly, wiring, firmware installation, and calibration—helping you build a reliable, precise, and cost-effective CNC milling machine for DIY production.
Explore how much plastic CNC machining costs and what factors influence pricing — from material selection to machining time and finishing. Learn how to choose the right supplier and reduce costs while maintaining precision and efficiency.
Learn how much custom CNC machining costs and what key factors affect pricing. Explore materials, machining time, tolerances, finishing, and cost-saving strategies to make your CNC machining projects more competitive, efficient, and reliable for global manufacturing.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour in India and what factors impact pricing. Explore cost comparisons by machine type, region, and material. Understand how to calculate expenses, reduce costs, and source high-precision CNC machining services for your manufacturing projects worldwide.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour for wood, including cost factors, price ranges, and optimization strategies. This guide explains machine types, materials, and efficiency methods for achieving precise, cost-effective results in wood CNC machining.
Learn how many zero points are used in CNC machining and why they are vital for precision, speed, and efficiency. Explore machine, work, and tool coordinate systems, setup methods, and advanced zero-point automation for smarter production.