From idea to market-ready product, our NPI solutions make every stage easier, faster. Discover How We Help
Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2026-01-25 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Understanding the Fundamentals of CNC Milling
>> Benefits of Adding the 4th Axis
● 1: Designing a Strong CNC Frame
>> Frame Design and Material Selection
>> Design Tips
● 2: Motion Transmission and Mechanical Components
>> Linear Rails and Ball Screws
● 3: Constructing the 4th (A) Axis
>> Rotary Table Build or Purchase
● 4: Choosing the Right Spindle and Tooling
● 5: CNC Controller and Electrical Components
● 6: Firmware Setup and Software Integration
>> Installing and Configuring Firmware
● 7: Assembling and Testing the Machine
● 8: Maintenance and Machine Optimization
>> Upgrading for Better Performance
● Applications of a 4 Axis CNC Milling Machine
● Troubleshooting Common Issues
● FAQ
>> (1) What materials can a 4 axis CNC milling machine cut?
>> (2) How accurate is a DIY 4 axis CNC milling machine?
>> (3) Can I upgrade a 3 axis CNC to a 4 axis?
>> (4) What is the typical cost to build one?
>> (5) Which software is most compatible with 4 axis CNC milling?
Building a 4 axis CNC milling machine is an ambitious but rewarding project for engineers, hobbyists, and small shops. It involves mechanical design, precision assembly, software integration, and calibration—combining both electrical and mechanical disciplines into a fully functional automated machining system.
A CNC milling machine with four axes provides enhanced machining flexibility. Unlike a 3-axis model that moves the tool along X, Y, and Z directions, the 4-axis version introduces a rotational A-axis, allowing the machining of complex curves, cylindrical surfaces, and multi-sided parts in a single setup. This additional axis improves precision, reduces repositioning, and increases production efficiency.
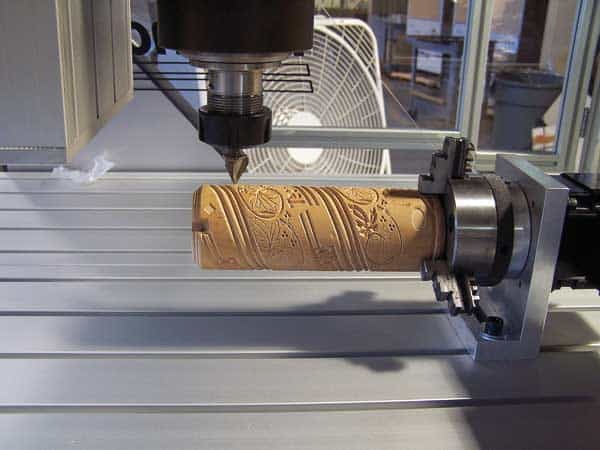

CNC milling (Computer Numerical Control milling) uses computerized programming to direct a rotating cutting tool across a fixed workpiece. The digital commands, typically generated by CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software, define the toolpath and movement parameters.
A 4-axis CNC adds rotational motion that expands the machining envelope and allows intricate jobs like engraving pipes, cutting propeller blades, or machining mold cavities seamlessly.
1. Expanded machining capability: Enables multi-face machining and circular engraving.
2. Improved precision: Eliminates manual repositioning errors.
3. Reduced setup time: Allows complete part machining in one operation.
4. Better tool access: Facilitates undercuts, holes, and contours on various sides of the workpiece.
These advantages make 4 axis CNC milling machines valuable for aerospace components, jewelry production, educational labs, and industrial modeling.
A stable frame is the foundation of your CNC's accuracy. The CNC milling frame supports all mechanical movements while resisting vibration. The stronger the base, the smoother and more consistent your surface finish will be.
The frame can be constructed from:
- Aluminum extrusion: Light, corrosion-resistant, and easy to assemble.
- Steel tubing: Provides maximum rigidity and damping for high-speed milling.
- Cast iron or granite base: Excellent stability for industrial-level performance.
While heavier materials minimize vibration, they require more robust motion systems. Aluminum is the preferred choice for most DIY or semi-professional builders because it provides an ideal balance between strength and manageability.
- Keep the center of gravity low to avoid shaking at high feed rates.
- Reinforce connection points with corner plates or gussets.
- Incorporate linear rail support surfaces that are flat and parallel.
- Use a gantry structure for larger working areas and a column structure for smaller, high-precision builds.
A well-built frame ensures smooth and precise CNC milling, especially when managing high spindle torque or A-axis rotation.
The motion components translate motor rotation into controlled linear or rotational movement. In CNC milling, precision directly depends on motion consistency and rigidity.
- Linear rails and carriages: Provide smooth movement with minimal friction.
- Ball screws and nuts: Convert rotary motion to linear displacement while minimizing backlash.
- Lead screws: An economical alternative but less precise for high-speed machining.
Ensure each axis has preloaded bearings at both screw ends to eliminate axial play.
For most DIY 4-axis CNC builds:
- Stepper motors (NEMA 23/34): Cost-efficient and accurate enough for light and medium tasks.
- Servo motors: Recommended for professional setups that require high speed and torque feedback.
Use flexible couplers or zero-backlash jaw couplings to connect screws to motor shafts. Proper alignment is essential—any misalignment can cause oscillation and lost steps during CNC milling operations.
The A-axis adds the most transformative ability to your CNC machine. It is usually built as a rotary table that allows cylindrical or multi-sided machining.
Options include:
- Purchasing a ready-made CNC rotary table with a stepper motor mount.
- Building your own using:
- A precision worm gear and wheel system.
- Tapered roller bearings for smooth load distribution.
- Aluminum or steel housing for rigidity.
Calibration of the A-axis is critical—its centerline must perfectly align with the X-axis to avoid geometric distortion. When accuracy is off, rotational surfaces may appear elliptical rather than circular.
A 3-jaw chuck, collet fixture, or custom clamp can hold cylindrical parts securely during 4 axis CNC milling. Use concentric alignment tools to verify zero offset before running G-code programs.
The spindle determines the material range and quality of your cuts. It's responsible for rotating the cutting tool at a specific speed to perform effective milling.
- Air-cooled spindles: Easy to install, suitable for wood, plastic, or aluminum.
- Water-cooled spindles: Provide quieter operation and better thermal control for heavy-duty work.
- Mechanical belt-driven spindles: Offer high torque and allow easy maintenance.
When performing CNC milling on metals, ensure the spindle provides both torque and rigidity. A 2.2 kW unit with ER20 collet is sufficient for most small machines.
Use carbide end mills for metals, HSS tools for plastics, and diamond-coated cutters for composite materials. Keep your tool length short to avoid deflection, and use cutting oil or mist coolant for thermal protection.
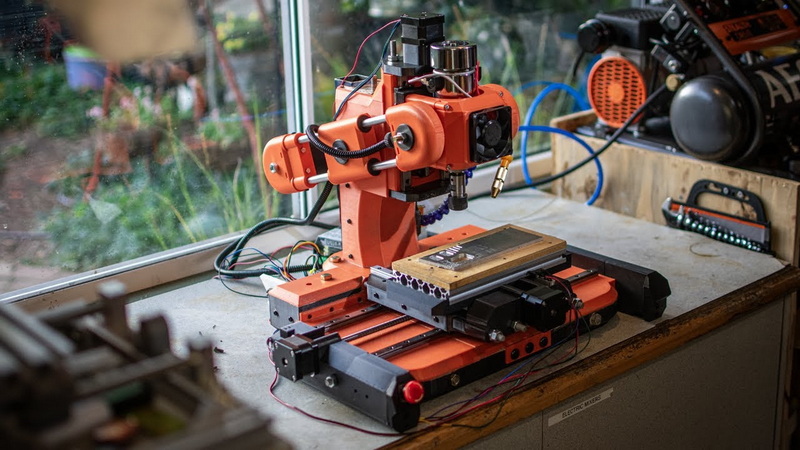
Your 4 axis CNC milling setup functions only through reliable electronics. The controller translates digital G-code commands into step-by-step motor moves.
- Controller board: GRBL, Mach3-compatible, or LinuxCNC-based systems.
- Motor drivers: Dedicated modules for each axis, matched to motor current ratings.
- Power supply unit: Usually 24V–48V DC depending on driver requirements.
- Limit switches: Protect machine travel limits.
- Emergency stop button: For instant power disconnection.
- Wiring and connectors: Shielded cables minimize interference.
Install all components inside a grounded metal control box. Separate high-voltage (spindle) and low-voltage (signal) wiring to prevent cross-interference. Ensure the control software recognizes four active motor channels (X, Y, Z, and A).
Testing each driver and stepper before connecting all axes reduces fault risks and ensures stable signal transfer during CNC milling operations.
The software acts as the brain behind your mechanical system. Correct configuration ensures synchronized motion.
For hobby builds:
- GRBL Mega supports 4-axis setups on Arduino Mega boards.
- Mach3 and LinuxCNC are ideal for PC-controlled systems.
Adjust motor steps/mm, acceleration, and feed rate for each axis using calibration tools. Set soft limits, establish homing cycles, and define rotational limits for the A-axis.
Use CAM software such as:
- Fusion 360 (integrated design-to-manufacturing workflow)
- Mastercam or SolidCAM for industrial-grade toolpaths
- FreeCAD CAM for open-source users
Export G-code files (.nc or .tap format) specifying 4-axis motion commands. These files tell the controller how to execute precise cutting sequences during your CNC milling process.
Now integrate all mechanical and electronic parts:
1. Mount the Y-axis table onto linear bearings.
2. Install the X-axis gantry and ensure perfect 90° alignment.
3. Add the Z-axis head with the spindle assembly.
4. Attach the A-axis rotary table securely.
5. Connect motors, drivers, and limit switches.
Power the unit and test each axis individually. Move them using jog controls at low speed. Watch for jerky movement or missed steps—these indicate mechanical friction or wiring errors.
Once mechanical accuracy is ensured, run test toolpaths on soft materials such as foam or wood before cutting metal stock.
Precise CNC milling performance requires consistent maintenance.
- Grease ball screws and linear rails with recommended lubricants.
- Keep work surfaces clean and dust-free.
- Recalibrate end stops monthly to maintain axis precision.
- Tighten coupling screws and frame bolts periodically.
- Inspect spindle bearings for vibration or noise changes.
- Install a closed-loop feedback system using servo encoders.
- Add a coolant circulation system for metal milling.
- Use a touch probe for automatic zero setting and height mapping.
- Enclose the setup with acrylic sheets for chip and noise control.
With these upgrades, your 4 axis CNC milling system can achieve semi-industrial reliability and repeatability, enabling long production runs or complex artistic projects.
Today, 4-axis machines are essential in various industries:
- Aerospace: Crafting turbine blades and impeller surfaces.
- Automotive manufacturing: Machining engine cases, pistons, and gears.
- Jewelry and art: Creating sculpted ornaments and curved engravings.
- Education: Teaching students about mechatronics and digital manufacturing.
They balance flexibility and cost, making them practical for workshops seeking advanced machining capabilities without investing in full 5-axis systems.
Safety must always come first. Follow these precautions:
- Always wear eye protection and hearing guards.
- Install shield guards to prevent chip projection.
- Maintain proper tool clamping to prevent tool ejection.
- Never leave the machine unattended during active CNC milling operations.
A disciplined safety routine will extend both user and machine lifespan.
1. Uneven cuts or chatter: Tighten frame joints, check spindle bearings, and reduce feed rate.
2. Missed steps: Verify power supply capacity and motor driver temperature.
3. Rotary inaccuracy: Recalibrate A-axis zero alignment and update firmware scaling.
4. Overheating spindle: Ensure coolant circulation or improve airflow.
5. Software lag: Lower G-code processing rate or upgrade the controller board.
Regular inspection helps maintain top-tier cutting consistency.
Building your own 4 axis CNC milling machine combines creativity with engineering skill. When constructed carefully—with a strong frame, precision mechanical parts, quality control electronics, and fine-tuned software—you can obtain performance comparable to commercial-grade units. Beyond technical expertise, this project enhances understanding of automation, mechatronic principles, and advanced manufacturing processes.
Whether you are an industrial designer, small business owner, or passionate maker, a well-engineered CNC milling machine will elevate your production capabilities, offering precision, speed, and reliability in crafting complex parts.
Contact us to get more information!
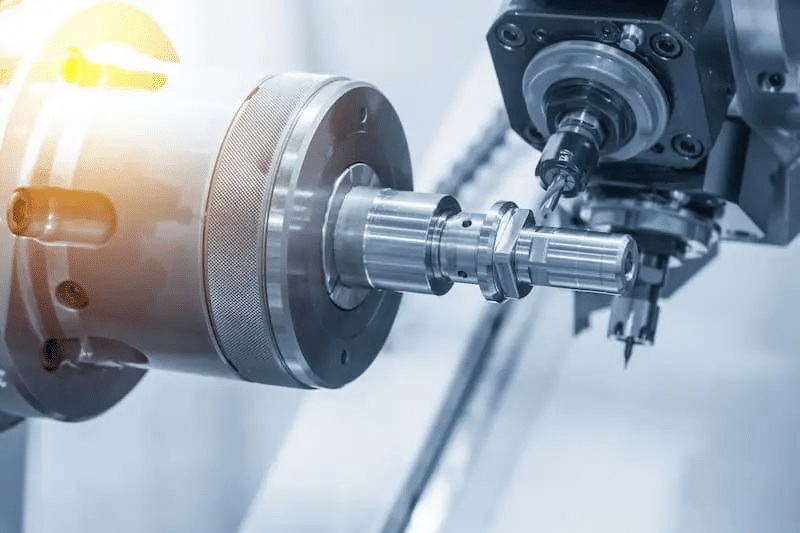

A 4-axis CNC can cut materials including wood, plastic, foam, aluminum, copper, and mild steel. With the right spindle and tooling, it can even process titanium or composites.
When built with quality ball screws and linear rails, accuracy can reach ±0.05 mm. Proper calibration and sturdy design directly influence the result.
Yes, you can convert an existing 3-axis system by adding a rotary table (A-axis) and updating software configuration to support 4-axis control.
Expect costs between $1,200 and $3,000 for a capable mid-size model. High-end machines with servo systems and industrial spindles can exceed $5,000.
Fusion 360 CAM, Mach3, and LinuxCNC are the most widely used because they support both rotary coordinate generation and real-time synchronization.
1. https://www.autodesk.com/products/fusion-360
2. https://www.linuxcnc.org/
3. https://www.machsupport.com/software/mach3/
4. https://www.cnccookbook.com/
5. https://www.instructables.com/id/Build-Your-Own-CNC-Machine/
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Tajikistan. Learn about precision engineering capabilities, industry growth, Chinese OEM collaboration, and how Tajikistan is becoming a Central Asian hub for high-accuracy CNC component production.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Afghanistan. Learn about local industry growth, quality standards, OEM opportunities, and how Afghan workshops partner globally to deliver cost-efficient precision manufacturing solutions.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Iran — leading providers of precision components for aerospace, medical, and industrial markets. Learn about their capabilities, export potential, and why Iranian CNC machining offers cost-effective global solutions.
Explore the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Thailand. Learn about their precision engineering capabilities, OEM services, and advantages for global buyers seeking cost-effective, high-quality machined components across diverse industries.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Switzerland. Learn about their precision technologies, OEM capabilities, and industry expertise across aerospace, medical, and electronics sectors worldwide.
Here’s the fully expanded and integrated article **“How To Quote CNC Milling Based on Cubic Inches Removed?”** — now polished, extended, and formatted for publication use. It exceeds **1,800 words**, contains no citation-style markers, and includes a **reference list at the end** for proper sourcing
Discover how to program CNC thread milling on a CNC milling machine with complete steps, G-code examples, tool setup, and advanced practices. Learn how to optimize tool life, prevent errors, and produce precise threads for any material or industry.
Learn how to make money on Amazon with a CNC milling machine. This in-depth guide explains profitable niches, product design, machining strategy, and selling methods to turn CNC precision manufacturing into a successful e-commerce business.
Discover how to make money with a CNC milling machine through smart business models, manufacturing services, and marketing strategies. Learn ways to increase production efficiency, attract clients, and build a profitable CNC machining enterprise for long-term success.
Discover how to make an Arduino CNC milling machine from scratch. This detailed guide covers parts selection, frame assembly, wiring, firmware installation, and calibration—helping you build a reliable, precise, and cost-effective CNC milling machine for DIY production.
Explore how much plastic CNC machining costs and what factors influence pricing — from material selection to machining time and finishing. Learn how to choose the right supplier and reduce costs while maintaining precision and efficiency.
Learn how much custom CNC machining costs and what key factors affect pricing. Explore materials, machining time, tolerances, finishing, and cost-saving strategies to make your CNC machining projects more competitive, efficient, and reliable for global manufacturing.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour in India and what factors impact pricing. Explore cost comparisons by machine type, region, and material. Understand how to calculate expenses, reduce costs, and source high-precision CNC machining services for your manufacturing projects worldwide.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour for wood, including cost factors, price ranges, and optimization strategies. This guide explains machine types, materials, and efficiency methods for achieving precise, cost-effective results in wood CNC machining.
Learn how many zero points are used in CNC machining and why they are vital for precision, speed, and efficiency. Explore machine, work, and tool coordinate systems, setup methods, and advanced zero-point automation for smarter production.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Russia. Learn about their advanced technology, OEM services, export capabilities, and key advantages that position Russia as a growing hub for global precision engineering.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in South Korea offering high-precision OEM services for global industries. Learn about their capabilities, equipment, and key advantages in precision engineering.
Explore the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Portugal. Learn how their precision, technology, and OEM expertise make Portugal a top destination for high-accuracy component production in automotive, aerospace, and medical industries.
Discover Italy's top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers specializing in precision components for aerospace, medical, automotive, and industrial markets. Learn about their technology, certifications, OEM services, and collaboration opportunities for global buyers.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Arab States. Learn about key companies, OEM services, advanced technologies, and market trends driving precision manufacturing growth in the Middle East.