From idea to market-ready product, our NPI solutions make every stage easier, faster. Discover How We Help
Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2026-01-25 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Understanding CNC Milling Machines
>> Essential Design Parameters
● 3: Installing Linear Motion Components
● 4: Choosing Motors and Drive Systems
>> Servo Motors
>> Power and Electronics Setup
● 5: Adding the Spindle and Cutting Tools
● 6: Wiring and Electronic Control
>> Software Linked to CNC Milling
● 8: Safety Precautions and Testing
● 9: Tuning and Performance Optimization
>> Performance Enhancement Tips
● 10: Maintenance for Long-Term Use
● 11: Common Troubleshooting Tips
● FAQ
>> (1) What materials can a CNC milling machine cut?
>> (2) How accurate can a DIY CNC milling machine be?
>> (3) Which software is best for CNC milling?
>> (4) Can I upgrade a 3-axis CNC to 4-axis?
>> (5) How should I maintain my CNC milling machine?
Building a 3D CNC milling machine from scratch is one of the most satisfying projects for any engineer or maker. It combines the disciplines of mechanical design, electronics, software control, and precision machining into a unified system. The reward is the ability to fabricate complex 3D components, custom prototypes, and functional parts directly in your own workshop.
In this guide, you'll learn how to design, assemble, calibrate, and optimize a complete 3D CNC milling setup capable of cutting metals, plastics, and composites with high accuracy.
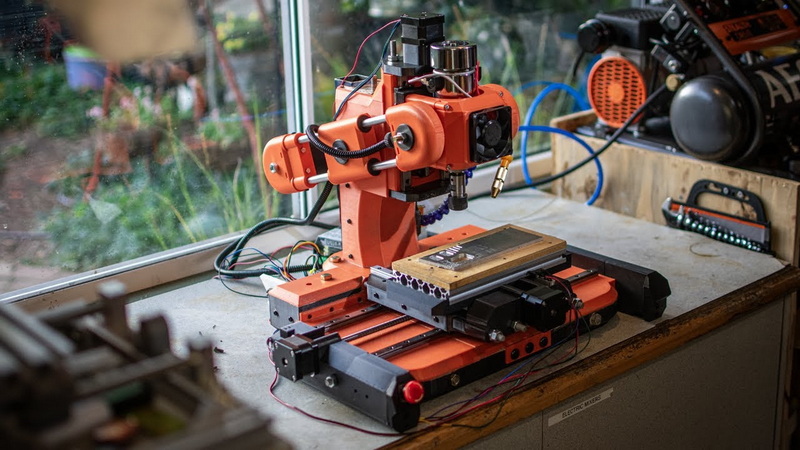
CNC milling stands for Computer Numerical Control milling, an automated machining process that uses coded instructions to guide a rotating cutting tool along multiple axes to remove material from a solid workpiece. Unlike manual milling, CNC machines follow digital blueprints to achieve repeatable precision and intricate shapes.
A 3D CNC milling system typically consists of three linear axes — X, Y, and Z — that allow movement in three directions. Together, these enable the machine to produce contoured surfaces, 3D carvings, and precision molds. Advanced systems may add a fourth or fifth axis for rotational movement, increasing flexibility and speed in complex operations.
Modern CNC milling machines rely on the synergy between mechanical stability, strong motors, accurate sensors, and efficient G-code interpretation. The more rigid and well-tuned your machine, the higher the quality and repeatability of your cuts.
Before you buy parts or cut materials, create a precise design plan. Planning determines the machine's size, accuracy, and material compatibility.
- Purpose: Define whether your CNC will cut wood, aluminum, or steel. Harder materials require stronger frames and higher torque motors.
- Travel Range: Determine how far each axis should move. The X-axis length defines workpiece width, the Y-axis determines depth, and the Z-axis controls height.
- Rigidity: Machine rigidity affects the quality of cuts. Flexing structures produce uneven surfaces.
- Cost vs. precision: A more accurate CNC milling system usually costs more but saves time during calibration and machining.
Use tools like *Fusion 360*, *SolidWorks*, or *FreeCAD* to model the frame, motor mounts, spindle position, and tool paths. A digital representation helps visualize motion limits and anticipate mechanical stress points.
Your CNC milling frame acts as the skeleton of the entire system. It must be both stable and vibration-resistant.
- Steel: Strongest and most rigid, suitable for metalworking CNC milling machines but heavy and difficult to machine.
- Aluminum: Lighter and easier to cut, perfect for hobby or semi-professional builds. Provides adequate stiffness for aluminum and plastic machining.
- MDF or plywood: Low-cost option for beginners building their first machine, though less durable and prone to vibration.
- Epoxy granite or composite: High-end solutions with excellent vibration damping characteristics.
1. Cut all frame sections precisely according to the CAD model.
2. Assemble the base using bolts, corner brackets, or welding.
3. Ensure each section meets at 90-degree angles using machinist squares.
4. Install cross-bracing on long beams to reduce flex.
5. Mount a solid base board or T-slot table on top.
A properly built frame establishes stability and alignment, preventing tool chatter and ensuring a smoother milling surface during long runs.
The linear motion system is the engine of precision for your CNC milling machine. It transforms motor rotation into smooth, controlled linear travel.
- Ballscrews or leadscrews: Drive the axes with minimal backlash. Ballscrews are preferred for precision due to low friction.
- Linear rails and bearings: Guide axis motion while maintaining alignment. Rail stiffness defines machining accuracy.
- Couplers: Connect screw shafts to motor shafts, ideally flexible couplers that absorb slight misalignment.
- Bearing blocks: Support screw ends and distribute load evenly.
High-quality rails and screws might raise the budget, but they yield exponentially better performance and reliability. When assembling, use precision shims or alignment jigs to ensure rail straightness.
The CNC milling drive system controls accuracy and speed. Stepper or servo motors translate control signals into movement.
- Easy to use and affordable.
- Suitable for 3-axis hobby CNC milling machines.
- Common sizes: NEMA 17, 23, or 34.
- Require matching drivers (such as TB6600 or DM542).
- Offer closed-loop feedback and faster speeds.
- Feature higher torque and smoother motion.
- Ideal for larger or industrial 3D CNC milling systems.
1. Calculate current draw and voltage requirements for all axes.
2. Choose drivers that can handle at least 25% more current than motor ratings.
3. Select a stable DC power supply, typically 24V–48V.
4. Mount electronic components on a protected, ventilated panel.
Balanced tuning of acceleration, velocity, and microstepping in your control software ensures efficient motion without missed steps or jerky behavior.
The spindle acts as the heart of CNC milling operations — spinning the cutting tool at thousands of RPM to shape materials.
- DC spindle (300–800W): Lightweight, ideal for wood or acrylic.
- AC spindle (1.5–2.2kW): Heavy-duty choice for aluminum and soft metals.
- Water-cooled models: Quieter and maintain temperature during long runs.
- Air-cooled models: Simplify installation, though louder.
Mount your spindle on a Z-axis carriage using adjustable clamps, allowing fine-tuning of tool height and angle. Balance the spindle carefully to avoid vibration and misalignment during cutting.
Choose the right end mill geometry based on material:
- 1–2 flute mills for plastics and wood.
- 3–4 flute mills for aluminum or brass.
- Carbide-coated tools for hardened steel.
Having multiple bit types allows smoother results and less wear during extended CNC milling sessions.
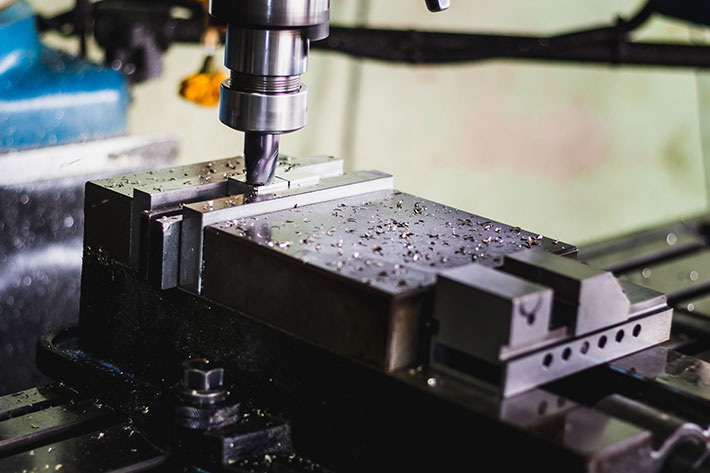

Your electronics system links motors, limit switches, spindle speed control, and the main controller. Proper wiring ensures consistent signal communication and safety.
- CNC controller board: Arduino GRBL shield, Mach3 board, or industrial controller.
- Motor drivers: Convert control signals into power for motors.
- Limit switches: Define axis boundaries to prevent overtravel.
- Emergency stop button: Mandatory for safety compliance.
- Cable management: Route power and signal lines separately to prevent electromagnetic interference.
Label all connections, use terminal blocks or connectors for easy replacement, and shield cables with braided sleeving.
Once the hardware is complete, focus on programming the CNC to respond accurately to commands.
- CAD Software: Fusion 360, AutoCAD, or SolidWorks to design parts.
- CAM Software: Converts 3D designs into tool paths (G-code). Popular choices include Fusion 360, VCarve Pro, and Aspire.
- CNC Control Software: Mach3, LinuxCNC, or Candle to run your machine.
1. Set steps per millimeter: Adjust each axis until movement matches distances in software.
2. Check backlash: Modify nuts, couplings, or compensation settings to reduce drift.
3. Align (tram) the spindle: Keep the spindle perpendicular to the bed.
4. Level the worktable: Use a dial gauge to check flatness across travel.
5. Run test cuts: Mill a small calibration pattern to validate precision.
Accurate calibration ensures flawless part geometry and maximizes tool life.
Safety is crucial in CNC milling environments, as moving machinery and rotating tools present real hazards.
- Wear protective gear: goggles, ear defenders, and dust masks.
- Keep wires and moving parts shielded.
- Incorporate emergency stops on both hardware and software levels.
- Avoid operating the CNC unattended during initial testing.
- Ensure good ventilation when cutting plastic or composite materials.
Perform a “dry run” — running your G-code without cutting material — to confirm motion paths and avoid tool crashes.
After initial testing, fine-tune performance for smoother, more accurate CNC milling results.
- Increase microstepping for finer resolution.
- Reduce feed rate for delicate materials.
- Use vibration dampers or additional frame braces.
- Install anti-backlash nuts on leadscrews.
- Calibrate spindle RPM for optimal chip load.
You can upgrade your DIY CNC milling system with automatic touch probes or sensors for tool height detection, ensuring deeper integration with advanced CNC workflows.
Even a well-built CNC milling machine requires consistent maintenance to remain reliable over time.
- Clean debris from rails and workspace after each use.
- Lubricate bearings, leadscrews, and linear guides regularly.
- Inspect wiring every few weeks for loose connectors.
- Store cutting tools dry and free from corrosion.
- Re-level the bed if you notice inconsistent depths.
Preventive maintenance not only extends lifetime but also keeps the CNC's precision stable across different projects.
Beginners often face small alignment or software issues. Here are some common problems and solutions:
- Backlash noise or vibration: Check coupler alignment and tighten all bolts.
- Motors skipping steps: Lower acceleration settings or check driver current.
- Uneven cutting depth: Recalibrate Z-axis zero and ensure bed surface is flat.
- Tool breakage: Reduce feed rate or spindle speed, and check tool material compatibility.
- Software crashes: Ensure G-code is post-processed correctly for your controller.
Learning to diagnose these issues quickly saves time and improves accuracy during ongoing CNC milling operations.
Constructing your own 3D CNC milling machine may seem complex, but with patience, careful design, and step-by-step assembly, it's entirely achievable. Each stage — from frame building to spindle calibration — contributes to the overall precision and repeatability of your system.
The finished machine empowers you to produce intricate components from a wide variety of materials, transforming digital designs into tangible, high-quality parts. As your experience grows, you can integrate automatic tool changers, rotary axes, or sensor-based feedback systems to elevate your CNC milling performance to an advanced level.
Contact us to get more information!

A CNC milling machine can effectively machine wood, plastics, acrylics, brass, and soft metals like aluminum. Higher-powered spindles allow cutting of mild steel with proper cooling.
A well-calibrated CNC milling unit can achieve positioning accuracy between ±0.03 to ±0.05 mm, sufficient for most mechanical and prototype projects.
Fusion 360 offers an all-in-one CAD/CAM platform ideal for beginners and professionals. Alternatives include Aspire for artistic carving and Mach3 for motion control.
Yes. Adding a rotary A-axis provides an extra rotational movement, allowing your machine to carve cylindrical or complex shapes with improved flexibility.
Clean debris, lubricate all motion parts, and check alignments regularly. Replace worn bearings and cutting tools promptly to maintain performance.
1. https://www.autodesk.com/products/fusion-360
2. https://wiki.linuxcnc.org/
3. https://www.machsupport.com/
4. https://www.hubs.com/knowledge-base/what-cnc-milling/
5. https://www.buildyourcnc.com/
6. https://reprap.org/wiki/CNC_Milling_Machine
Learn how to find workplace coordinates for CNC machining through manual and automated methods. Discover G54–G59 offsets, touch probe usage, and best practices for ensuring precision, accuracy, and repeatability in CNC manufacturing.
Discover how to perform accurate hole-shaft fits in CNC machining. Learn types of fits, tolerance systems, machining steps, precision inspection, and assembly validation to achieve perfect mechanical performance and repeatable dimensional accuracy.
Learn how to determine X Y step in CNC machining with complete calibration methods, formulas, and real examples. This detailed guide explains how to ensure precision motion, improve dimensional accuracy, and maintain long-term machine consistency.
This detailed guide explains how to clean CNC machining tooling marks from plexi edges using sanding, buffing, flame polishing, and vapor polishing techniques. Learn how to prevent edge defects, achieve optical clarity, and maintain pristine CNC-machined acrylic surfaces.
Discover how to automate CNC machining for maximum efficiency, precision, and cost savings. Learn about robotics integration, IoT sensors, AI-driven software, and workflow strategies to transform your manufacturing process into a fully automated, data-powered production system.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Tajikistan. Learn about precision engineering capabilities, industry growth, Chinese OEM collaboration, and how Tajikistan is becoming a Central Asian hub for high-accuracy CNC component production.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Afghanistan. Learn about local industry growth, quality standards, OEM opportunities, and how Afghan workshops partner globally to deliver cost-efficient precision manufacturing solutions.
Discover the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Iran — leading providers of precision components for aerospace, medical, and industrial markets. Learn about their capabilities, export potential, and why Iranian CNC machining offers cost-effective global solutions.
Explore the top Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Thailand. Learn about their precision engineering capabilities, OEM services, and advantages for global buyers seeking cost-effective, high-quality machined components across diverse industries.
Discover the leading Swiss-type CNC machining manufacturers and suppliers in Switzerland. Learn about their precision technologies, OEM capabilities, and industry expertise across aerospace, medical, and electronics sectors worldwide.
Here’s the fully expanded and integrated article **“How To Quote CNC Milling Based on Cubic Inches Removed?”** — now polished, extended, and formatted for publication use. It exceeds **1,800 words**, contains no citation-style markers, and includes a **reference list at the end** for proper sourcing
Discover how to program CNC thread milling on a CNC milling machine with complete steps, G-code examples, tool setup, and advanced practices. Learn how to optimize tool life, prevent errors, and produce precise threads for any material or industry.
Learn how to make money on Amazon with a CNC milling machine. This in-depth guide explains profitable niches, product design, machining strategy, and selling methods to turn CNC precision manufacturing into a successful e-commerce business.
Discover how to make money with a CNC milling machine through smart business models, manufacturing services, and marketing strategies. Learn ways to increase production efficiency, attract clients, and build a profitable CNC machining enterprise for long-term success.
Discover how to make an Arduino CNC milling machine from scratch. This detailed guide covers parts selection, frame assembly, wiring, firmware installation, and calibration—helping you build a reliable, precise, and cost-effective CNC milling machine for DIY production.
Explore how much plastic CNC machining costs and what factors influence pricing — from material selection to machining time and finishing. Learn how to choose the right supplier and reduce costs while maintaining precision and efficiency.
Learn how much custom CNC machining costs and what key factors affect pricing. Explore materials, machining time, tolerances, finishing, and cost-saving strategies to make your CNC machining projects more competitive, efficient, and reliable for global manufacturing.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour in India and what factors impact pricing. Explore cost comparisons by machine type, region, and material. Understand how to calculate expenses, reduce costs, and source high-precision CNC machining services for your manufacturing projects worldwide.
Learn how much CNC machining costs per hour for wood, including cost factors, price ranges, and optimization strategies. This guide explains machine types, materials, and efficiency methods for achieving precise, cost-effective results in wood CNC machining.
Learn how many zero points are used in CNC machining and why they are vital for precision, speed, and efficiency. Explore machine, work, and tool coordinate systems, setup methods, and advanced zero-point automation for smarter production.