From idea to market-ready product, our NPI solutions make every stage easier, faster. Discover How We Help
Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2025-12-11 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Understanding Your Project Requirements
● Evaluating 3D Printing Technologies
>> Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
>> Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
>> Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS)
● Considering Material Options
● Accuracy, Tolerance, and Surface Finish
● Turnaround Time and Production Speed
● Pricing Transparency and Value for Money
● Customer Support and Technical Assistance
● Quality Assurance and Certifications
● Online Platforms vs. Local Manufacturers
● Environmental Sustainability
● FAQ
>> 1. What are the main factors that determine print quality?
>> 2. Which is better for industrial applications: SLS or MJF?
>> 3. Can I supply my own materials to a 3D printing service?
>> 4. How do I protect my design's intellectual property?
>> 5. What post-processing options are most effective?
Choosing the right 3D printing service is a crucial decision that directly influences the success of your project. Today's market offers countless providers—ranging from small local workshops to large-scale online platforms that cater to industrial production. Each service differs in terms of materials, technologies, pricing structures, and quality assurance. Therefore, understanding your needs and knowing what to evaluate is key to finding a reliable partner. This detailed guide covers every aspect of selecting the most suitable 3D printing service, from defining requirements to analyzing pricing transparency and after-sales support.

The first step in the selection process is clarifying your project goals. Without a defined purpose, even the most advanced printing technology cannot guarantee satisfactory results.
- Application Purpose: Determine if your project involves prototyping, visual modeling, functional parts, or final production. Prototypes demand flexibility and low-cost materials, while production-ready parts require high precision and strength.
- Design Requirements: Consider size limitations, layer resolutions, and structural complexities. Certain technologies handle intricate geometries better than others.
- Production Scale: Are you printing a single prototype or dozens of functional units? Scalability impacts cost, lead time, and process selection.
- Mechanical and Aesthetic Expectations: Think about part durability, texture, and finishing quality. These details influence which materials and machines are appropriate.
- Budget Limitations: Define a realistic cost range early so you can compare pricing models efficiently.
Having a clear project outline allows you to communicate your expectations effectively to any potential provider.
3D printing involves various techniques, each optimized for certain material behaviors and project purposes. Recognizing their differences helps you identify which service aligns best with your objectives.
FDM is the most common and cost-effective technology. It works by melting thermoplastic filaments and extruding them layer by layer. FDM printers specialize in rapid prototyping but may leave visible layer lines. Ideal for design validation, educational models, and hobby projects.
SLA uses UV lasers to cure liquid resin into solid layers. It provides remarkable surface detail and smooth finishes, perfect for miniature models, dental components, and jewelry. However, SLA parts require post-curing and can be brittle under stress.
SLS fuses polymer powder with a laser, creating strong, functional parts without support structures. The results are durable, lightweight, and consistent—suitable for mechanical assemblies and complex enclosures.
MJF enhances SLS by applying fusing and detailing agents, achieving uniform strength and texture. It excels at producing batches of end-use parts with excellent resolution and consistent performance.
DMLS caters to high-performance engineering sectors. It builds fully dense metal parts, suitable for aerospace, automotive, and medical applications. The process supports titanium, stainless steel, and aluminum for robust and heat-resistant components.
PolyJet technology sprays resin droplets that cure instantly under UV light, allowing multi-material and multi-color production. This method is ideal for presentation models where aesthetic appeal is critical.
Material selection defines not only the strength but also the visual appearance and post-processing potential of your part. When choosing a provider, investigate their inventory and whether they offer specialized or certified materials.
- Thermoplastics (ABS, PLA, PETG): Affordable and versatile; perfect for prototypes and small product runs.
- Engineering Plastics (Nylon, Polycarbonate): Deliver durability and flexibility for mechanical parts.
- Resins (Standard, Tough, Flexible, Transparent): Offer excellent detail and visual quality for artistic and display pieces.
- Metals (Aluminum, Titanium, Stainless Steel): Support structural performance and longevity in industrial designs.
- Composites (Carbon Fiber, Kevlar): Provide strength-to-weight advantages ideal for drone or robotic parts.
- Biocompatible Materials: Essential for medical and dental use where safety and certification are required.
Advanced services usually provide data sheets that outline tensile strength, heat resistance, and elasticity, helping you make data-driven decisions.
Dimensional precision plays a major role in mechanical assemblies. Reliable 3D printing services should clearly communicate achievable tolerances and surface quality.
- Layer Resolution: Finer layers create smoother surfaces. A resolution of 50 microns or less is considered high quality.
- Tolerance Range: Industrial-grade printers can maintain tolerances within ±0.1 mm, ensuring accurate fits.
- Surface Finish Options: Services may offer sanding, bead-blasting, vapor smoothing, or coating for visual enhancement.
- Testing and Verification: Some companies provide technical inspection reports for mission-critical projects.
Always request a sample or reference part before placing a bulk order to evaluate real-world quality and tactile feel.
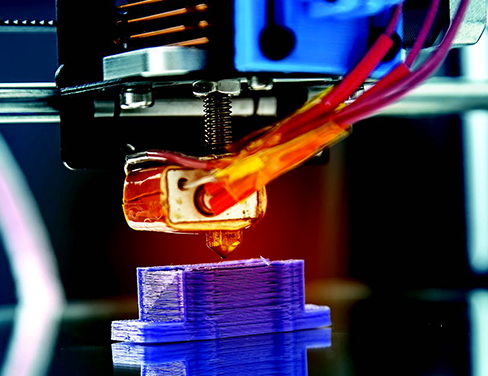
For fast-paced product development, turnaround time is critical. It depends on print volume, material type, and queue capacity.
- Prototype Orders: Typically completed within 1–3 days.
- Batch Manufacturing: Larger runs or metal printing may take a week or more.
- Express Services: Many providers offer expedited production for an additional fee.
- Shipping Logistics: Verify delivery options and transit times. Delays in logistics can offset fast printing times.
Efficiency often reveals how established and well-managed a 3D printing company truly is.
The price of a 3D printed part depends on several variables—volume, material, geometry complexity, and required finishing steps. Reliable services maintain transparent pricing models.
- Volume-Based Pricing: Larger objects or higher quantities often lower per-unit cost.
- Material Weight: Since materials like metals or composites are expensive, precision in design helps minimize waste.
- Design Optimization: Request feedback from providers to reduce cost without compromising function.
- Hidden Fees: Ensure no additional costs exist for support removal, polishing, or post-processing unless stated.
Compare quotes across at least three providers while reviewing online reviews or portfolio samples. The cheapest option may not always deliver consistent quality.
Good communication defines the quality of your collaboration. Reliable services offer technical guidance before and after printing.
- Design Review: Some services analyze CAD files to confirm printability and structural soundness.
- Communication Speed: Evaluate how quickly the team responds to inquiries or quotations.
- Expertise of Staff: Access to engineers or designers ensures professional explanations and solutions.
- After-Sales Support: Ask about post-print troubleshooting, replacements, or warranty policies.
Strong, responsive communication prevents errors and ensures smoother workflow throughout your project lifecycle.
Consistency is a hallmark of professional-grade 3D printing. Certifications signify adherence to strict quality management systems.
- ISO 9001 or AS9100 Certifications: Guarantee rigorous process and quality control.
- Inspection Protocols: Some services employ coordinate measuring machines (CMM) to verify precision.
- Material Traceability: Providers should record batch numbers and verification data for industrial accountability.
- Internal Testing: Tensile or stress testing ensures functional reliability.
These practices become especially important when you need repeat orders or are producing safety-critical parts.
The decision between online platforms and local workshops depends on your project scale, communication preferences, and urgency.
- Online Platforms: Offer instant quoting tools, wide material selection, and global delivery. However, communication can feel impersonal.
- Local Workshops: Provide face-to-face collaboration, immediate feedback, and easier logistics for urgent changes.
- Hybrid Models: Some online platforms partner with regional factories, combining scale efficiency with local responsiveness.
Balancing convenience, cost, and control helps determine which option fits your workflow best.
Modern industries emphasize eco-friendly manufacturing. Many 3D printing materials and processes now aim to minimize waste and energy consumption.
- Material Recycling: Some services recycle failed prints or scraps into reusable filament.
- Biodegradable Filaments: PLA and other bio-based materials reduce environmental impact.
- Energy Efficiency: New printing technologies and smart scheduling reduce carbon emissions.
- Sustainable Practices: Partnering with greener providers enhances your brand's ecological image.
Customers increasingly value sustainability, making it a differentiator when selecting a 3D printing provider.
Before finalizing your choice, check online testimonials, customer reviews, and case studies.
- Project Portfolios: Industry-specific examples (e.g., automotive or medical) showcase capability.
- Ratings and Feedback: Look for consistent positive remarks on reliability, accuracy, and support.
- Client References: Request references or verified samples for high-value orders.
- Repeat Business Indicators: Companies with a strong returning customer base often deliver dependable quality.
Transparent reviews reflect real-world results, helping you avoid costly trial and error.
Choosing the right 3D printing service involves more than picking the lowest quote. It requires understanding your project goals, exploring different printing technologies, evaluating available materials, and ensuring consistent quality. Always assess the provider's support, transparency, and certification to ensure your printed parts meet both functional and aesthetic standards. When you take time to research and compare services, you ensure lasting partnerships and successful, reliable outcomes.

Print quality depends on printer calibration, layer resolution, material choice, and operator experience. High-end industrial printers generally yield better precision and finish.
Both produce durable nylon parts, but MJF offers faster production and smoother finishes, while SLS provides greater flexibility for large, complex components.
Some providers allow this if compatible with their equipment. However, certification and testing may be required to guarantee safe operation and consistent results.
Reputable companies often sign non-disclosure agreements (NDAs) to safeguard your 3D files. Always confirm their data-handling and confidentiality policies before submission.
Common methods include bead blasting, painting, polishing, and anodizing for metals. The optimal process depends on desired aesthetics and functional goals.
Is CNC machining expensive? This detailed guide breaks down every factor influencing CNC cost—from materials and machine time to tolerances and production volume—while offering expert strategies to reduce expenses and maximize manufacturing efficiency.
This in-depth article explores whether CNC machining is dangerous, detailing potential hazards, critical safety measures, advanced automation, and operator best practices. It also covers regulatory standards, sustainability, and includes a comprehensive FAQ on CNC safety management.
This comprehensive article examines whether CNC machining qualifies as blue-collar work. It traces the role's history, skills, and education, highlighting its evolution into a gray-collar profession that fuses craftsmanship, technology, and digital competence in modern manufacturing.
This article explores whether CNC machining is a dying trade. It concludes that far from disappearing, CNC machining is evolving with automation, AI, and Industry 4.0 integration. The trade remains vital to global manufacturing, offering lasting opportunities for innovation and skilled careers.
This complete guide explains how to start and grow a CNC machining business — from planning, financing, and equipment selection to marketing, automation, and sustainability. Learn expert strategies to build a profitable precision manufacturing company in today's competitive market.
Explore South Korea's leading CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Learn about their technology, expertise, and industries served. Ideal for OEMs, wholesalers, and partners seeking precision engineering and high-quality custom machining solutions.
Discover why Portugal is emerging as a leader among CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Explore its top machining companies, precision technologies, and global OEM collaborations delivering high-quality, cost-effective components for industries worldwide.
Explore Italy's leading CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Discover their technical expertise, key companies, industry capabilities, and why global OEMs rely on Italian CNC machining for precision, innovation, and long-term partnership opportunities.
An in-depth look at how CNC milling is transforming manufacturing across the Arab States. This article explores top CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers, their technologies, challenges, partnerships, and the growing role of precision machining in regional industrial strategy.
Discover the top CNC milling services manufacturers and suppliers in France. Explore their technology, quality standards, international collaborations, and industry advantages for precision parts manufacturing and OEM production partnerships.
Explore the top 10 Prototype CNC Machining Manufacturers in China. Featuring Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd., this detailed guide covers their strengths, capabilities, and why Chinese CNC machining companies lead in global innovation and precision manufacturing.
Discover the Top 10 Precision CNC Machining Manufacturers in China, highlighting their strengths, technologies, and OEM capabilities. Featuring Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. as a leader, this guide helps global buyers find reliable CNC partners for precision engineering projects.
Explore the top 10 Custom CNC Machining Manufacturers in China, led by Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. Learn about each company's strengths, capabilities, and quality standards to find the ideal CNC machining partner for your custom OEM projects.
China's top Rapid CNC Machining Manufacturers, led by Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd., lead the world in precision, quality, and speed. This article reviews the top 10 companies driving China's rapid manufacturing future through innovation and advanced CNC technology.
Explore the top 10 Laser Engraving Services Manufacturers in China, featuring industry leader Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. Learn about capabilities, OEM customization, and key factors for choosing the best laser engraving partner for your business.
This detailed guide explains every step for setting a CNC turning machine—from preparation and workpiece mounting to tooling, programming, testing, and maintenance. Ideal for machinists seeking precision, safety, and efficiency in CNC turning operations.
Learn step-by-step how to make a CNC turning program in Hindi. Understand G-codes, M-codes, roughing and finishing cycles, and advanced techniques for precision machining. Perfect for Hindi-speaking students, machinists, and beginners in CNC operation.
This detailed guide explains step-by-step how to build a CNC turning machine, from mechanical design to electronic integration and software setup. It covers calibration, maintenance, safety, and troubleshooting, offering a comprehensive roadmap for engineers and hobbyists alike.
This extended guide thoroughly explains how to lock speed and feed in Fanuc CNC turning machines using parameters, custom M-codes, ladder logic, and password protection. It provides step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting advice, and best practices to achieve greater process stability and quality control.
This comprehensive guide explains how to perform eccentric turning on CNC machines, covering setup, programming, balancing, tooling, inspection, and safety. It includes examples, troubleshooting tips, and FAQs to help machinists achieve accurate, vibration-free eccentric machining operations.