From idea to market-ready product, our NPI solutions make every stage easier, faster. Discover How We Help
Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2025-12-12 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Understanding CNC Turning Basics
● Materials and Tools Required
● 1: Designing the CNC Turning Machine
● 2: Building the Machine Frame
● 3: Installing the Spindle Assembly
● 4: Assembling the Tool Carriage and Tool Post
● 5: Integrating the Electronics
● 6: Software and Control Configuration
● 7: Calibration and Precision Testing
● 10: Troubleshooting Common Issues
● Advantages of Building Your Own CNC Turning Machine
>> Key Benefits
● FAQ
>> (1) What is the main purpose of a CNC turning machine?
>> (2) How much does it cost to build a CNC turning machine?
>> (3) Can CNC turning machines work with multiple materials?
>> (4) Which software is best for beginners in CNC machine control?
>> (5) How can I improve cutting accuracy and surface finish?
Building a CNC turning machine is a comprehensive engineering challenge that merges mechanical design, electrical control, and digital programming into a functional whole. CNC, short for Computer Numerical Control, uses precise computer commands to guide machining movements. A CNC turning machine—also referred to as a CNC lathe—rotates a workpiece at high speed while a cutting tool removes material to create symmetrical parts.
For engineers, hobbyists, and students, constructing such a machine from scratch is both educational and practical. It deepens understanding of mechanical systems, improves knowledge of automation, and offers a hands-on way to produce custom parts. This guide walks through the essential steps: planning, design, mechanical assembly, electronics integration, calibration, and maintenance.
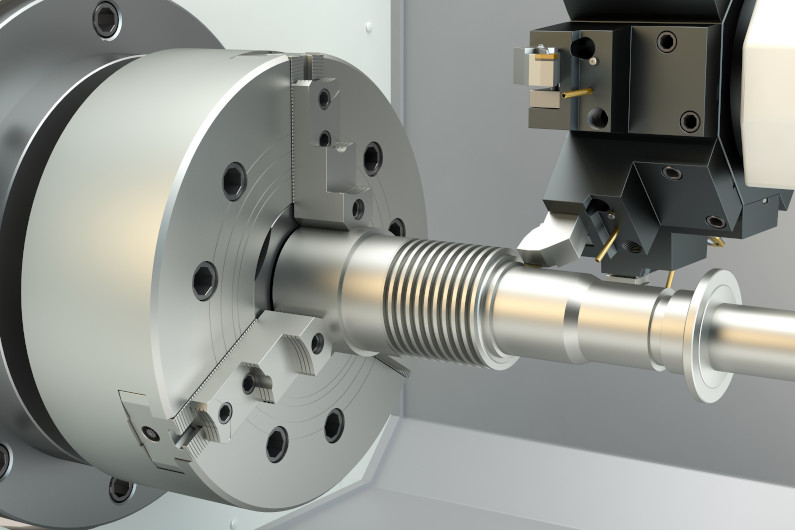
In a CNC turning process, the workpiece spins on an axis while a stationary cutting tool carves away layers of material. The system follows G-code, a universal programming language that instructs the machine on positioning, feed rates, and spindle speeds.
These machines excel at producing cylindrical or conical shapes with flawless accuracy. Every movement—whether the spindle rotation or the tool's linear travel—is translated from digital commands into mechanical motion. This automation eliminates the inconsistencies of manual lathes and enables mass production with repeatable results.
To design one successfully, you need a solid grasp of key mechanical systems: how spindles transmit rotary power, how bearings stabilize motion, how ball screws convert rotation to linear travel, and how electronics translate code into motion control.
Before any construction begins, it's critical to secure durable, high-precision components and appropriate tools.
- Frame and bed: The backbone of the machine, typically made of welded steel or cast iron for vibration resistance.
- Headstock and spindle assembly: Includes a spindle shaft, motor, and bearing system.
- Tailstock: Supports the other end of long workpieces for balanced turning.
- Carriage and cross-slide: Holds the tool post and moves it along X and Z axes.
- Ball screws: Accurate transmission elements that precisely move the carriage.
- Linear guide rails: Provide smooth and low-friction motion.
- Chuck or collet: Secures the workpiece to the spindle.
- Coolant pump and enclosure: Maintain temperature and improve safety.
- Stepper or servo motors: Convert electrical signals into motion.
- Motor drivers and power supply: Controls voltage and current to each motor.
- CNC controller or microcontroller: The “brain” of the machine.
- VFD (Variable Frequency Drive): Adjusts the spindle motor's rotation speed.
- Wires, connectors, relays, and limit switches: Create safety and feedback circuits.
- Emergency stop button: Provides immediate power cutoff.
Precision matters, and quality tools ensure alignment and safety:
- Calipers, micrometers, and dial gauges.
- Drills, taps, and welding equipment.
- Screwdrivers, Allen keys, and torque wrenches.
- Soldering tools for circuit assembly.
- Computer with CAD/CAM and CNC control software.
Begin with a well-structured design phase using CAD software such as SolidWorks, Fusion 360, or AutoCAD. Every joint, shaft, and bearing should be modeled accurately to predict performance before physical fabrication.
- Rigidity: Ensure minimal frame deflection, as small vibrations can affect tolerance.
- Travel ranges: Define the desired X-axis and Z-axis movement based on your part sizes.
- Motion ratio: Match motor torque to required feed forces.
- Spindle speed: Choose an optimal RPM range for different materials.
- Heat management: Include cooling paths and air vents.
- Ease of maintenance: Design access panels for belt adjustments or lubrication.
Digital simulation or finite element analysis can verify the structural stability before beginning fabrication.
The frame supports every functional unit, so focus on precision assembly. Begin by cutting and welding steel plates into a stable rectangular base.
1. Frame Fabrication: Align and weld panels to eliminate torsional twist.
2. Stress Relief: Heat-treat the welded structure to minimize internal stress.
3. Rail Mounting: Bolt linear guide rails accurately to machined surfaces.
4. Cross-Slide Setup: Attach cross-slide carriage and confirm smooth travel.
5. Leveling: Adjust foot screws to achieve perfect alignment.
A sturdy base reduces noise, vibration, and wear on moving parts. Consider filling the frame with epoxy granite for additional damping on larger builds.
The spindle performs high-speed rotation and requires precision bearings—angular contact or tapered roller bearings are best.
- Machine the headstock bore precisely for tight bearing fits.
- Set up a multi-pulley or direct belt drive linked to the spindle motor.
- Ensure the spindle runs concentrically using a dial gauge.
- Install a chuck that can easily interchange with collet systems.
- Attach a safety guard and coolant nozzles around the spindle.
High-quality lubrication and correct preload of bearings improve performance and longevity.
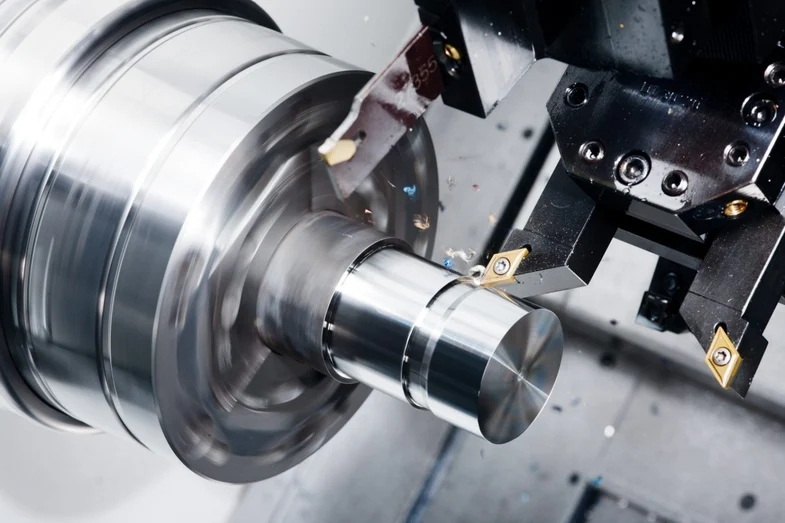

The carriage travels along the bed, holding tools in adjustable holders. This movement defines accuracy in cutting.
- Install the ball screws and nut housings with minimal backlash.
- Mount linear bearings for smooth X and Z axis motion.
- Connect stepper or servo motors to each axis with flexible couplings.
- Attach the tool post, capable of automatic or manual tool change.
- Verify axis orthogonality using a square and indicator.
Lubricate rails and screws consistently to maintain surface finish, especially under heavy loads.
The electrical system converts digital data into motion. It consists of three layers: power supply, controller, and actuators.
1. Mount electronic components inside a steel cabinet with airflow.
2. Supply dedicated power lines: low voltage for control, high current for motors.
3. Connect motors to their drivers following manufacturer pin diagrams.
4. Ground all components to prevent static discharge.
5. Integrate limit switches, relays, and sensors with the controller board.
6. Test individual axes using manual jogging commands.
Label all wires and protect them using cable conduits to avoid damage. Shielded signal cables minimize electrical interference during high-frequency switching.
The machine requires software to interpret G-code into motion commands. Depending on your budget and preference, Mach3, LinuxCNC, or GRBL can serve as control platforms.
- Input physical dimensions of X and Z axes.
- Set motor parameters: steps per revolution, pitch, and acceleration.
- Define limit switch positions to calibrate travel boundaries.
- Upload tool offset and spindle speed tables.
- Perform test runs with virtual simulation mode before live cutting.
For G-code generation, CAD/CAM tools like Fusion 360 or Mastercam can automate toolpaths from 3D models, producing efficient machining sequences.
Even a well-assembled machine needs fine-tuning. Calibration guarantees that software coordinates match actual tool positions.
- Use a dial test indicator for positioning checks.
- Measure backlash and apply compensation values in software.
- Verify circle accuracy by turning a test piece and measuring deviation.
- Adjust spindle speed via VFD feedback for consistent RPM.
- Perform endurance tests to check thermal expansion stability.
Accuracy refinement can achieve tolerances under ±0.01 mm with proper alignment.

A CNC turning machine involves sharp tools, spinning parts, and electrical systems. Establish safety measures before operation.
- Always close the protective cover when the spindle runs.
- Use proper grounding and surge protection.
- Keep coolant drains clean to prevent clogs.
- Apply lubricants daily and check for leaks.
- Turn off the power before repairing or adjusting any part.
- Inspect belts, screws, and couplings weekly.
- Replace bearings or seals that show wear.
- Clean chips and dust to avoid contamination.
- Relevel the frame yearly for long-term accuracy.
- Store G-code backups and firmware settings.
An organized maintenance plan not only extends machine life but also ensures smooth operation for years.
After your CNC lathe becomes fully functional, consider upgrading for improved precision and automation.
- Install a touch probe for automated part measurement.
- Add an automatic tool changer (ATC) for multi-tool operations.
- Use linear encoders for closed-loop feedback on motor positions.
- Implement coolant mist systems for high-speed turning.
- Upgrade to ethernet-based controllers for faster data processing.
These enhancements elevate machining capacity closer to industrial-grade performance.
No build is flawless at first. Here are frequent issues and practical troubleshooting approaches:
- Axis skipping or vibration: Recheck motor current, adjust driver microsteps, and tighten couplings.
- Poor surface finish: Verify tool sharpness and spindle alignment.
- Overheating motor: Reduce acceleration settings and ensure adequate cooling.
- Software communication error: Update drivers or check USB cable shielding.
- Dimensional inaccuracy: Recalibrate steps per millimeter in the control software.
Document each resolved issue; keeping a maintenance and troubleshooting log helps detect patterns and prevent future errors.
Building a CNC lathe from scratch offers more than cost savings—it gives full control over design, features, and upgrading options.
- Flexible customization: Adapt the working area, motor type, and spindle power to your projects.
- Lower costs: Commercial CNC lathes can cost tens of thousands, but a DIY build can achieve similar precision for a fraction of the price.
- Educational value: Gain practical skills in mechatronics, control systems, and manufacturing.
- Repairability: Every part is known and replaceable without proprietary barriers.
- Personal achievement: The satisfaction of seeing a home-built machine produce accurate parts is unmatched.
Though the setup requires effort and patience, it rewards builders with autonomy and advanced understanding of industrial systems.
Constructing a CNC turning machine blends mechanics, electronics, and computer control into a cohesive system capable of precise automated cutting. Through careful design, sturdy frame building, precise spindle alignment, thorough calibration, and consistent maintenance, you can achieve accuracy and performance comparable to industrial-grade machines.
Whether for small workshops, educational laboratories, or prototype production, a DIY CNC lathe demonstrates the power of engineering creativity. With discipline and attention to detail, you can create a tool that represents both craftsmanship and technological innovation—an authentic expression of engineering mastery.
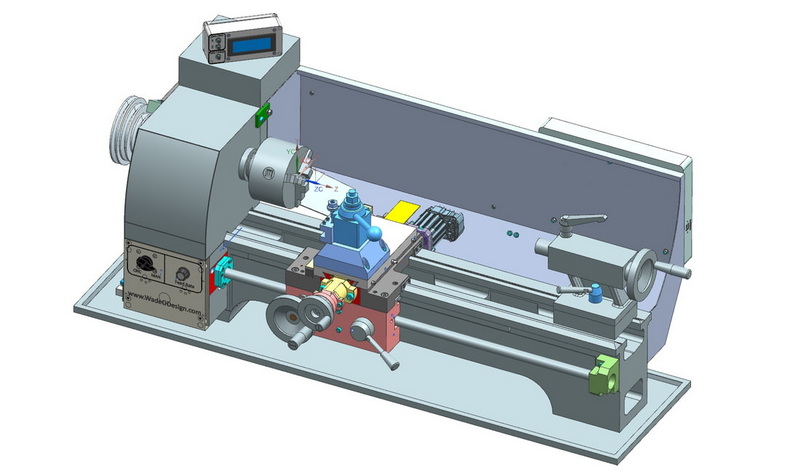
A CNC turning machine automates rotational cutting processes, producing precise cylindrical parts such as rods, bolts, and bushings. It reduces manual labor and ensures high consistency in production.
A small-scale DIY build typically ranges from $1,000 to $3,000, while larger or industrial-level designs may cost $10,000 or more, depending on material grade, motor specifications, and control systems.
Yes. They can handle metals like aluminum, brass, copper, and steel, as well as plastics such as ABS, acrylic, and nylon. The only requirement is using suitable cutting tools and speed settings for each material.
For beginners, GRBL (Arduino-based) is simple and cost-effective. For advanced users, Mach3 and LinuxCNC offer better flexibility, plug-in support, and industrial compatibility.
Ensure proper frame rigidity, stable spindle bearings, and high-quality cutting tools. Maintain consistent tool lubrication, balance rotating parts, and fine-tune feed rate and RPM parameters during operation.
Is CNC machining expensive? This detailed guide breaks down every factor influencing CNC cost—from materials and machine time to tolerances and production volume—while offering expert strategies to reduce expenses and maximize manufacturing efficiency.
This in-depth article explores whether CNC machining is dangerous, detailing potential hazards, critical safety measures, advanced automation, and operator best practices. It also covers regulatory standards, sustainability, and includes a comprehensive FAQ on CNC safety management.
This comprehensive article examines whether CNC machining qualifies as blue-collar work. It traces the role's history, skills, and education, highlighting its evolution into a gray-collar profession that fuses craftsmanship, technology, and digital competence in modern manufacturing.
This article explores whether CNC machining is a dying trade. It concludes that far from disappearing, CNC machining is evolving with automation, AI, and Industry 4.0 integration. The trade remains vital to global manufacturing, offering lasting opportunities for innovation and skilled careers.
This complete guide explains how to start and grow a CNC machining business — from planning, financing, and equipment selection to marketing, automation, and sustainability. Learn expert strategies to build a profitable precision manufacturing company in today's competitive market.
Explore South Korea's leading CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Learn about their technology, expertise, and industries served. Ideal for OEMs, wholesalers, and partners seeking precision engineering and high-quality custom machining solutions.
Discover why Portugal is emerging as a leader among CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Explore its top machining companies, precision technologies, and global OEM collaborations delivering high-quality, cost-effective components for industries worldwide.
Explore Italy's leading CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Discover their technical expertise, key companies, industry capabilities, and why global OEMs rely on Italian CNC machining for precision, innovation, and long-term partnership opportunities.
An in-depth look at how CNC milling is transforming manufacturing across the Arab States. This article explores top CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers, their technologies, challenges, partnerships, and the growing role of precision machining in regional industrial strategy.
Discover the top CNC milling services manufacturers and suppliers in France. Explore their technology, quality standards, international collaborations, and industry advantages for precision parts manufacturing and OEM production partnerships.
Explore the top 10 Prototype CNC Machining Manufacturers in China. Featuring Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd., this detailed guide covers their strengths, capabilities, and why Chinese CNC machining companies lead in global innovation and precision manufacturing.
Discover the Top 10 Precision CNC Machining Manufacturers in China, highlighting their strengths, technologies, and OEM capabilities. Featuring Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. as a leader, this guide helps global buyers find reliable CNC partners for precision engineering projects.
Explore the top 10 Custom CNC Machining Manufacturers in China, led by Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. Learn about each company's strengths, capabilities, and quality standards to find the ideal CNC machining partner for your custom OEM projects.
China's top Rapid CNC Machining Manufacturers, led by Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd., lead the world in precision, quality, and speed. This article reviews the top 10 companies driving China's rapid manufacturing future through innovation and advanced CNC technology.
Explore the top 10 Laser Engraving Services Manufacturers in China, featuring industry leader Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. Learn about capabilities, OEM customization, and key factors for choosing the best laser engraving partner for your business.
This detailed guide explains every step for setting a CNC turning machine—from preparation and workpiece mounting to tooling, programming, testing, and maintenance. Ideal for machinists seeking precision, safety, and efficiency in CNC turning operations.
Learn step-by-step how to make a CNC turning program in Hindi. Understand G-codes, M-codes, roughing and finishing cycles, and advanced techniques for precision machining. Perfect for Hindi-speaking students, machinists, and beginners in CNC operation.
This detailed guide explains step-by-step how to build a CNC turning machine, from mechanical design to electronic integration and software setup. It covers calibration, maintenance, safety, and troubleshooting, offering a comprehensive roadmap for engineers and hobbyists alike.
This extended guide thoroughly explains how to lock speed and feed in Fanuc CNC turning machines using parameters, custom M-codes, ladder logic, and password protection. It provides step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting advice, and best practices to achieve greater process stability and quality control.
This comprehensive guide explains how to perform eccentric turning on CNC machines, covering setup, programming, balancing, tooling, inspection, and safety. It includes examples, troubleshooting tips, and FAQs to help machinists achieve accurate, vibration-free eccentric machining operations.