From idea to market-ready product, our NPI solutions make every stage easier, faster. Discover How We Help
Views: 222 Author: Tomorrow Publish Time: 2025-12-10 Origin: Site
Content Menu
● Understanding CNC Milling Machines
● Key Components of a CNC Milling Machine
● Features That Define the Best CNC Milling Machine
>> 2. Spindle Speed, Power, and Torque
>> 3. Construction Quality and Rigidity
>> 4. Control Software and User Interface
>> 5. Automation and Sensor Technology
>> 6. Work Envelope and Machine Size
>> 7. Maintenance and Support Availability
● Advanced Performance Factors
● Top CNC Milling Machines in the Market
>> 1. Haas VF-2
>> 3. SYIL X7
>> 4. FANUC Robodrill α-D21MiB
>> 5. Bantam Tools Desktop CNC Milling Machine
● Choosing the Right CNC Milling Machine
● Emerging Trends in CNC Milling Technology
● How to Maintain a CNC Milling Machine
● FAQ
>> 1. What materials can CNC milling machines handle?
>> 2. How long does a CNC milling machine last?
>> 3. Are CNC milling machines difficult to learn for beginners?
>> 4. How accurate are CNC milling machines?
>> 5. What distinguishes 3-axis from 5-axis milling?
CNC milling machines have become indispensable in modern manufacturing, merging precision engineering with automation and digital control. These machines use Computer Numerical Control (CNC) to execute complex cutting, drilling, and shaping processes based on pre-programmed digital instructions. From aerospace engine parts to jewelry molds, CNC milling delivers accuracy, repeatability, and speed beyond the limits of manual machining.
Selecting the best CNC milling machine depends on multiple factors such as application type, performance requirements, and budget. This article explores what makes a milling machine exceptional, introduces top-performing models, and provides practical guidance for choosing the right one.
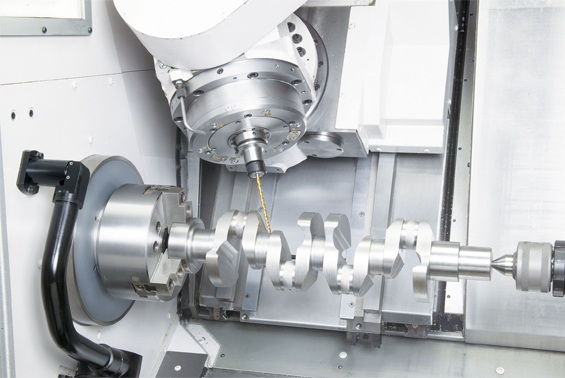
At its core, a CNC milling machine transforms raw material into precision parts through controlled cutting operations. Unlike manual milling, where an operator guides the tool, CNC milling interprets digital design files—usually CAD (Computer-Aided Design) models—into code such as G-code. The CNC controller reads this code and directs the milling head along precise coordinates.
These machines operate across multiple axes. Common configurations include:
- 3-axis CNC mills: Move along X, Y, and Z planes to create standard geometries.
- 4-axis machines: Add rotational movement for machining multiple faces without manual repositioning.
- 5-axis machines: Provide ultimate flexibility by tilting and rotating tools or workpieces for complex, curved, or organic designs.
The higher the number of axes, the greater the capability for intricate and precise manufacturing applications like impellers, orthopedic implants, and aerospace brackets.
Each CNC milling machine comprises essential parts that collectively dictate its accuracy, speed, and performance. Understanding these components helps when comparing models or diagnosing issues.
- Spindle: The spindle drives the cutting tool at controlled speeds. Its bearings, torque, and rotational stability define surface finish and precision.
- Table and bed: This platform supports the workpiece. The rigidity of the table reduces vibration, which influences accuracy.
- Axes drives and motors: Each axis uses servomotors or stepper motors to move the tool or table precisely based on digital commands.
- Tool changer: Automated tool changers (ATC) can hold and switch between several tools within seconds, increasing productivity.
- Control unit: The “brain” of the operation where users program, monitor, and adjust machining parameters.
- Coolant and lubrication systems: Cooling prevents tool wear and material deformation, crucial in machining hard metals.
- Enclosure and safety guards: Provide protection against flying chips and coolant splashes, essential for operator safety.
Together, these systems form the framework for machining consistency and overall usability.
When evaluating CNC milling machines, several technical and functional features determine their standing in the marketplace.
Machine rigidity, spindle alignment, and thermal stability all influence precision. The best CNC milling machines maintain tolerances as fine as ±0.002 mm, ensuring repeatable production for critical industries.
Spindle speed determines how fast the cutting tool rotates, while torque defines its cutting strength. Machines that regulate both automatically can adapt seamlessly between aluminum, stainless steel, or titanium.
High-performance models have variable-speed spindles ranging between 8,000–30,000 RPM, providing versatility for both finishing and rough cutting operations.
The frame material—usually cast iron or high-strength steel—absorbs vibrations. Precision-grade ball screws and linear guides further enhance stability. Poor construction often causes tool chatter, dimensional errors, and inconsistent finishes.
Modern CNCs pair with advanced CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software like Fusion 360, Mastercam, or Siemens NX. These systems streamline programming through simulation, collision detection, and direct G-code export. Machines supporting open-source or industry-standard protocols offer superior customization and training accessibility.
The latest CNC machines include automated tool changers, part probes, and real-time feedback systems. Sensors detect tool wear, temperature shifts, and spindle loads, enabling predictive maintenance and uninterrupted operation.
Desktop CNC mills are ideal for prototypes, jewelry, or PCB boards, while large industrial mills handle automotive frames or aircraft components. Choosing an appropriate work area prevents unnecessary costs or space limitations.
After-sales service, spare part supply, and software updates can make or break long-term usability. Investing in a brand with global support ensures uptime and minimal operational disruption.
Beyond the basics, several advanced engineering features separate superior machines from entry-level models:
- Thermal compensation: Sensors adjust tool paths based on temperature-induced expansion, improving dimensional precision.
- High-speed machining (HSM): This technology uses smaller cuts at faster feed rates, enhancing finish quality and reducing cycle times.
- Direct-drive spindles: Reduce mechanical losses and vibration by eliminating belt transmission.
- Simultaneous 5-axis control: Enables multi-surface machining without multiple setups, ideal for molds and turbine blades.
These innovations push CNC manufacturing toward higher productivity and flawless quality.
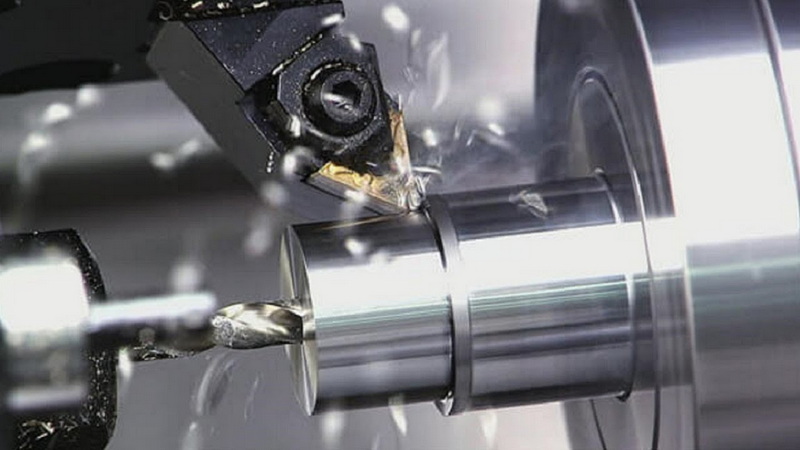

With numerous manufacturers competing globally, certain models consistently stand out for their engineering excellence and customer satisfaction.
Manufactured in the USA, the Haas VF-2 is a world-standard vertical machining center designed for strength and adaptability. With a 30-horsepower vector drive spindle and 1000 inches-per-minute rapid traverse rates, it's widely used in toolmaking and production facilities. The machine's robust cast-iron construction ensures stability for repeated precision machining.
For small-to-medium enterprises, the Tormach 1100MX offers professional capability at a manageable cost. It's powered by PathPilot control software, known for its intuitive interface and open programming. Capable of spindle speeds up to 10,000 RPM, it handles various materials efficiently. Its modular upgrades, such as an automatic tool changer and enclosure, add flexibility for evolving projects.
Compact and rugged, the SYIL X7 integrates industrial-grade Siemens or FANUC controllers with precision-machined cast components. It uses rigid tapping, automatic lubrication, and thermal balancing systems—ideal for continuous operation in small workshops and factories. Its footprint fits compact production lines without sacrificing accuracy.
Renowned for ultra-fast tool changes (as quick as 0.7 seconds), the FANUC Robodrill defines efficiency. It's commonly used for high-volume production of consumer electronics and precision components. The CNC system is known for reliability and minimal downtime, and FANUC's global support network enhances its appeal for professional environments.
The Bantam Tools desktop CNC is engineered for designers and education professionals. Despite its small size, it boasts high-speed spindles and aluminum milling capabilities. It integrates seamlessly with CAD software via cloud-based platforms, allowing users to create prototypes without specialized training.
A symbol of German engineering excellence, the DMG MORI DMU 50 offers simultaneous 5-axis machining for intricate geometry. With dynamic precision systems, high spindle speeds, and automation-ready design, it suits aerospace, automotive, and medical component manufacturing. Its rigidity and long lifecycle make it a favorite among global industries prioritizing ultimate accuracy.
This Japanese-built powerhouse delivers heavy-duty cutting and consistent accuracy. Its thermo-friendly concept stabilizes dimensional performance during long production runs. The GENOS series blends intelligent control with powerful spindle torque, making it suitable for metal fabrication and mold manufacturing.
Selecting the best CNC milling machine requires understanding both operational demands and financial parameters.
1. Identify purpose and production volume: A prototyping lab doesn't require industrial capacity, while high-volume manufacturers need durability and automation.
2. Match machine size to workspace: Larger work envelopes cost more and need more room.
3. Analyze software needs: Select models that integrate easily with your existing design ecosystem.
4. Check power supply and infrastructure: Certain machines require three-phase power and reinforced flooring.
5. Consider total cost of ownership: Beyond purchase price, include setup, tooling, maintenance, and software licensing.
Decision-making should balance capability and return on investment. Consulting with a vendor or technician before purchase ensures compatibility with current and future workloads.
The CNC industry evolves continuously as automation, AI, and sustainability converge. Several transformative trends are defining this era of advanced manufacturing:
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-driven systems adjust toolpaths in real time for higher efficiency and predictive failure prevention.
- Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining subtractive milling with additive 3D printing expands design possibilities.
- Smart Factory Connectivity: IoT-enabled mills transmit performance data for remote monitoring and resource optimization.
- Eco-friendly design: Regenerative braking, efficient coolant recycling, and energy-optimized servo motors promote sustainable operations.
- Collaborative Robotics: Cobots now assist CNC mills in loading, inspection, and part handling, improving workflow safety and reducing human fatigue.
As industries shift toward Industry 4.0, these advancements strengthen CNC milling's role at the core of smart, data-driven production ecosystems.
Proper maintenance ensures longevity and consistent output quality. Common best practices include:
- Routine cleaning: Remove chips, oil, and debris daily to maintain smooth operation.
- Lubrication: Check and refill lubrication systems regularly to prevent friction wear.
- Precision alignment checks: Perform monthly calibration to maintain axis accuracy.
- Spindle inspection: Monitor spindle noise and temperature for early failure detection.
- Software updates: Update firmware and control software to access the latest features and bug fixes.
Preventive maintenance reduces downtime and extends machine lifespan by several years—making it a critical part of any production strategy.
The best CNC milling machine is the one that aligns seamlessly with your production goals, skill level, and budget. For industrial applications, high-end models such as DMG MORI DMU 50 and Haas VF-2 stand out with their robustness, multi-axis capabilities, and precision. For cost-conscious innovators, Tormach 1100MX and SYIL X7 provide a perfect blend of accessibility and reliability.
As technology advances, features like smart sensors, AI integration, and hybrid machining redefine what's possible. Choosing the right machine means investing not only in equipment but in consistent precision, productivity, and innovation that drive long-term success.

CNC machines work with metals such as aluminum, copper, titanium, and steel, along with plastics, composites, and wood. The choice of cutting tools and spindle speed determines how efficiently each material can be processed.
Depending on workload and maintenance, most quality machines last 10 to 25 years. Regular lubrication, calibration, and careful handling extend this lifespan significantly.
Modern CNC interfaces and training materials make learning much easier. Entry-level software allows simulation-based training without risking material waste or tool damage.
High-precision machines achieve tolerances within ±0.002–0.005 mm. Accuracy varies with temperature control, tool wear, and spindle stability.
A 3-axis mill moves in three linear directions, ideal for flat or stepped surfaces. A 5-axis machine adds two rotational axes, allowing continuous machining of complex curved or angular surfaces in a single setup.
Discover why Portugal is emerging as a leader among CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Explore its top machining companies, precision technologies, and global OEM collaborations delivering high-quality, cost-effective components for industries worldwide.
Explore Italy's leading CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers. Discover their technical expertise, key companies, industry capabilities, and why global OEMs rely on Italian CNC machining for precision, innovation, and long-term partnership opportunities.
An in-depth look at how CNC milling is transforming manufacturing across the Arab States. This article explores top CNC Milling Services Manufacturers and Suppliers, their technologies, challenges, partnerships, and the growing role of precision machining in regional industrial strategy.
Discover the top CNC milling services manufacturers and suppliers in France. Explore their technology, quality standards, international collaborations, and industry advantages for precision parts manufacturing and OEM production partnerships.
Explore the top 10 Prototype CNC Machining Manufacturers in China. Featuring Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd., this detailed guide covers their strengths, capabilities, and why Chinese CNC machining companies lead in global innovation and precision manufacturing.
Discover the Top 10 Precision CNC Machining Manufacturers in China, highlighting their strengths, technologies, and OEM capabilities. Featuring Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. as a leader, this guide helps global buyers find reliable CNC partners for precision engineering projects.
Explore the top 10 Custom CNC Machining Manufacturers in China, led by Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. Learn about each company's strengths, capabilities, and quality standards to find the ideal CNC machining partner for your custom OEM projects.
China's top Rapid CNC Machining Manufacturers, led by Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd., lead the world in precision, quality, and speed. This article reviews the top 10 companies driving China's rapid manufacturing future through innovation and advanced CNC technology.
Explore the top 10 Laser Engraving Services Manufacturers in China, featuring industry leader Shenzhen Feifan Hardware & Electronics Co., Ltd. Learn about capabilities, OEM customization, and key factors for choosing the best laser engraving partner for your business.
This detailed guide explains every step for setting a CNC turning machine—from preparation and workpiece mounting to tooling, programming, testing, and maintenance. Ideal for machinists seeking precision, safety, and efficiency in CNC turning operations.
Learn step-by-step how to make a CNC turning program in Hindi. Understand G-codes, M-codes, roughing and finishing cycles, and advanced techniques for precision machining. Perfect for Hindi-speaking students, machinists, and beginners in CNC operation.
This detailed guide explains step-by-step how to build a CNC turning machine, from mechanical design to electronic integration and software setup. It covers calibration, maintenance, safety, and troubleshooting, offering a comprehensive roadmap for engineers and hobbyists alike.
This extended guide thoroughly explains how to lock speed and feed in Fanuc CNC turning machines using parameters, custom M-codes, ladder logic, and password protection. It provides step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting advice, and best practices to achieve greater process stability and quality control.
This comprehensive guide explains how to perform eccentric turning on CNC machines, covering setup, programming, balancing, tooling, inspection, and safety. It includes examples, troubleshooting tips, and FAQs to help machinists achieve accurate, vibration-free eccentric machining operations.
Learn how to post 3D printing services professionally with this comprehensive guide. Discover key steps for building an online presence, optimizing listings, managing orders, pricing smartly, and staying competitive in the fast-growing 3D printing market.
This extended guide explains how to market a 3D printing service through branding, SEO, content creation, social media, partnerships, and client experience. It provides actionable marketing strategies to build trust, improve visibility, and drive growth in a competitive 3D printing industry.
This comprehensive guide explains how to compare 3D printing services by analyzing key aspects such as technology options, materials, quality control, pricing transparency, delivery time, scalability, and security. It helps readers choose reliable providers for both prototypes and production parts.
An in-depth guide to choosing the right 3D printing service. Learn to evaluate technologies, materials, quality standards, and pricing. Perfect for engineers, designers, and entrepreneurs seeking reliable, precise, and cost-effective 3D printing solutions.
Discover how to effectively advertise 3D printing services using SEO, social media, paid campaigns, and branding. This comprehensive guide explains proven marketing strategies to grow your audience, attract clients, and build authority in the evolving 3D printing industry.
This in-depth article explains what defines the best CNC milling machine, highlighting critical technical features, top brands, maintenance tips, and emerging smart manufacturing trends. It concludes with expert advice and FAQs, guiding readers toward the ideal CNC solution for their needs.